Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy
- PMID: 31277692
- PMCID: PMC6612215
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-019-0754-1
Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy
Abstract
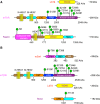
Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a protein kinase regulating cell growth, survival, metabolism, and immunity. mTOR is usually assembled into several complexes such as mTOR complex 1/2 (mTORC1/2). In cooperation with raptor, rictor, LST8, and mSin1, key components in mTORC1 or mTORC2, mTOR catalyzes the phosphorylation of multiple targets such as ribosomal protein S6 kinase β-1 (S6K1), eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1 (4E-BP1), Akt, protein kinase C (PKC), and type-I insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-IR), thereby regulating protein synthesis, nutrients metabolism, growth factor signaling, cell growth, and migration. Activation of mTOR promotes tumor growth and metastasis. Many mTOR inhibitors have been developed to treat cancer. While some of the mTOR inhibitors have been approved to treat human cancer, more mTOR inhibitors are being evaluated in clinical trials. Here, we update recent advances in exploring mTOR signaling and the development of mTOR inhibitors for cancer therapy. In addition, we discuss the mechanisms underlying the resistance to mTOR inhibitors in cancer cells.
Keywords: Cancer; Drug resistance; Oncogene; Targeted therapy; mTOR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

