The effect of deep or sustained remission on maintenance of remission after dose reduction or withdrawal of etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 31277720
- PMCID: PMC6610967
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-019-1937-4
The effect of deep or sustained remission on maintenance of remission after dose reduction or withdrawal of etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) are important options for managing rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Once patients achieve disease control, clinicians may consider dose reduction or withdrawal of the bDMARD. Results from published studies indicate that some patients will maintain remission; however, others will flare. We analyzed data from three etanercept down-titration studies in patients with RA to determine what extent of remission provides the greatest predictability of maintaining remission following dose reduction or discontinuation.
Methods: Patients with moderate to severe RA from the PRESERVE, PRIZE, and Treat-to-Target (T2T) randomized controlled trials were included. We determined the proportion of patients achieving remission with etanercept at the last time point in the induction period, and sustained remission (last two time points), according to the Disease Activity Score 28-joints (DAS28), the American College of Rheumatology (ACR)/European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) Boolean criteria, and the clinical disease activity index (CDAI). We also calculated the proportion achieving DAS28 deep remission (DAS28 ≤ 1.98), sustained deep remission (last two time points), and low disease activity (LDA), and LDA according to the CDAI. Then, we evaluated whether they maintained remission or LDA following etanercept dose reduction or withdrawal.
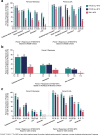
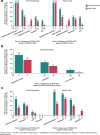
Results: Patients achieving sustained and/or deep remission were more likely than patients achieving remission or LDA to maintain remission/LDA after etanercept dose reduction or withdrawal. In PRESERVE, the proportions of patients with DAS28 sustained deep remission, deep remission, sustained remission, remission, and LDA who maintained remission following etanercept dose reduction were 81%, 67%, 58%, 56%, and 36%, respectively, P < 0.001 for trend. In PRESERVE, this trend was significant when etanercept was discontinued and when ACR/EULAR Boolean and CDAI remission criteria were used. Although some sample sizes were small, the PRIZE and T2T studies also demonstrated response trends according to ACR/EULAR Boolean and CDAI remission criteria, and T2T demonstrated response trends according to DAS28.
Conclusions: These results suggest that patients achieving disease control according to a stringent definition, such as sustained ACR/EULAR Boolean or CDAI remission, or a new definition of sustained deep remission by DAS28, have a higher probability of remaining in remission or LDA following etanercept dose reduction or withdrawal.
Trial registration: PRESERVE: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00565409 , registered 30 November 2007; PRIZE: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00913458 , registered 4 June 2009; T2T: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01578850 , registered 17 April 2012.
Keywords: ACR/EULAR Boolean; Anti-TNF; CDAI; DAS28; Dose reduction; Etanercept; Remission; Rheumatoid arthritis; Withdrawal.
Conflict of interest statement
YT has received speaking fees and/or honoraria from Daiichi-Sankyo, Astellas, Eli Lilly, Chugai, Sanofi, AbbVie, Pfizer, YL Biologics, Bristol-Myers, GlaxoSmithKline, UCB, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Novartis, Eisai, Takeda, Janssen, and Asahi-kasei and has received research grants from Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Bristol-Myers, Eisai, Chugai, Takeda, AbbVie, Astellas, Daiichi-Sankyo, Ono, MSD, and Taisho-Toyama. JSS has received research grant support from Abbott, BMS, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB and consultation and/or speaking honoraria from Abbott, Astra-Zeneca, BMS, Celgene, Celltrion, Glaxo, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung, Sanofi-Aventis, and UCB. HJ and LM were employees of Pfizer at the time the manuscript was written. AS is an employee of Syneos Health and was contracted by Pfizer to provide statistical support for the development of this paper. PE has received grant/research support and consultancy fees from AbbVie, BMS, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung, Sandoz, and UCB.
No nonfinancial competing interest exists for any author.
Figures

References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(6):960–977. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210715. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Nies JAB, Tsonaka R, Gaujoux-Viala C, Fautrel B, van der Helm-van Mil AHM. Evaluating relationships between symptom duration and persistence of rheumatoid arthritis: does a window of opportunity exist? Results on the Leiden early arthritis clinic and ESPOIR cohorts. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:806–812. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206047. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

