Mapping of Novel Leaf Rust and Stem Rust Resistance Genes in the Portuguese Durum Wheat Landrace PI 192051
- PMID: 31278174
- PMCID: PMC6686931
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.119.400292
Mapping of Novel Leaf Rust and Stem Rust Resistance Genes in the Portuguese Durum Wheat Landrace PI 192051
Abstract
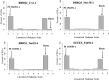
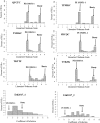
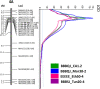
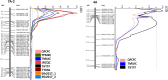
Leaf rust caused by Puccinia triticina Erikss. (Pt) and stem rust caused by Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici Erikss. & E. Henn (Pgt) are serious constraints to production of durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L). The objective of this study was to identify leaf rust resistance (Lr) and stem rust resistance (Sr) genes/QTL in Portuguese durum landrace PI 192051. Four Pt-isolates, representing three virulence phenotypes (BBBQJ, BBBSJ & EEEEE) and six Pgt-races TTKSK, JRCQC, TKTTF, QFCFC, TPMKC and TMLKC were used to evaluate 180 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from the cross Rusty (rust susceptible) × PI 192051-1 (rust resistant) at the seedling stage. The RILs were also phenotyped at the adult-plant stage in a stem rust nursery in Ethiopia in 2017. The RILs were genotyped using the Illumina iSelect 9K wheat SNP array. PI 192051-1 carries a previously unidentified major Sr gene designated as QSr.ace-7A on chromosome arm 7AS and Lr gene Lr.ace-4A in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 4A. In addition, three minor Sr QTL QSr.ace-1A, QSr.ace-2B and QSr.ace-4A were mapped in PI 192051-1 on chromosomes 1AL, 2BL, and 4A, respectively Lr.ace-4A could be co-located or tightly linked to QSr.ace-4A Markers linked to the identified QTL/genes can be used for marker assisted selection. These findings enrich the genetic basis of rust resistance in both durum and common wheat.
Keywords: DGGW; Ethiopia; Puccinia; QTL; SNP; disease resistance; food security; leaf rust; new resistance; wheat.
Copyright © 2019 Aoun et al.
Figures
References
-
- Ammar K., Lage J., Villegas D., Crossa J., Hernandez E. et al. , 2006. Association among durum wheat international testing sites and trends in yield progress over the last twenty two years. International Symposium on Wheat Yield Potential, Cd. Obregón, Sonora, Mexico, March 20–24th. Pp. 19–20.
-
- Aoun M., Kolmer J. A., and Acevedo M., 2018. Genotype by Sequencing for the Study of Population Genetics in Puccinia triticina Borlaug Global Rust Initiative Technical Workshop. Marrakech. Morocco, April 14–17. 10.13140/RG.2.2.33258.21444 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
