Zero-field nuclear magnetic resonance of chemically exchanging systems
- PMID: 31278303
- PMCID: PMC6611813
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10787-9
Zero-field nuclear magnetic resonance of chemically exchanging systems
Abstract
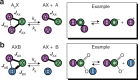
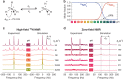
Zero- to ultralow-field (ZULF) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is an emerging tool for precision chemical analysis. In this work, we study dynamic processes and investigate the influence of chemical exchange on ZULF NMR J-spectra. We develop a computational approach that allows quantitative calculation of J-spectra in the presence of chemical exchange and apply it to study aqueous solutions of [15N]ammonium (15N[Formula: see text]) as a model system. We show that pH-dependent chemical exchange substantially affects the J-spectra and, in some cases, can lead to degradation and complete disappearance of the spectral features. To demonstrate potential applications of ZULF NMR for chemistry and biomedicine, we show a ZULF NMR spectrum of [2-13C]pyruvic acid hyperpolarized via dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization (dDNP). We foresee applications of affordable and scalable ZULF NMR coupled with hyperpolarization to study chemical exchange phenomena in vivo and in situations where high-field NMR detection is not possible to implement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correlation of high-field and zero- to ultralow-field NMR properties using 2D spectroscopy.J Chem Phys. 2021 Apr 14;154(14):144201. doi: 10.1063/5.0039294. J Chem Phys. 2021. PMID: 33858171
-
Zero- to ultralow-field nuclear magnetic resonance J-spectroscopy with commercial atomic magnetometers.J Magn Reson. 2020 May;314:106723. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2020.106723. Epub 2020 Apr 3. J Magn Reson. 2020. PMID: 32298993
-
A method for measurement of spin-spin couplings with sub-mHz precision using zero- to ultralow-field nuclear magnetic resonance.J Magn Reson. 2017 Nov;284:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2017.08.016. Epub 2017 Sep 1. J Magn Reson. 2017. PMID: 28961479
-
Applications of dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization in chemistry and biochemistry.Magn Reson Chem. 2018 Jul;56(7):566-582. doi: 10.1002/mrc.4735. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Magn Reson Chem. 2018. PMID: 29602263 Review.
-
Applications of dynamic nuclear polarization to the study of reactions and reagents in organic and biomolecular chemistry.Org Biomol Chem. 2010 Aug 7;8(15):3361-5. doi: 10.1039/c004420m. Epub 2010 Jun 17. Org Biomol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20556296 Review.
Cited by
-
Relayed hyperpolarization for zero-field nuclear magnetic resonance.Sci Adv. 2022 Jul 22;8(29):eabp9242. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abp9242. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35857837 Free PMC article.
-
Zero- to low-field relaxometry of chemical and biological fluids.Commun Chem. 2023 Aug 4;6(1):165. doi: 10.1038/s42004-023-00965-8. Commun Chem. 2023. PMID: 37542142 Free PMC article.
-
Interfacing Liquid State Hyperpolarization Methods with NMR Instrumentation.J Magn Reson Open. 2022 Jun;10-11:100052. doi: 10.1016/j.jmro.2022.100052. Epub 2022 Mar 10. J Magn Reson Open. 2022. PMID: 35530721 Free PMC article.
-
Digital quantum simulation of NMR experiments.Sci Adv. 2023 Nov 15;9(46):eadh2594. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adh2594. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37976365 Free PMC article.
-
Zero-Field NMR of Urea: Spin-Topology Engineering by Chemical Exchange.J Phys Chem Lett. 2021 Nov 4;12(43):10671-10676. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c02768. Epub 2021 Oct 27. J Phys Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 34705470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levitt, M. H. Spin Dynamics: Basics of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 2nd edn. (John Wiley & Sons, 2008).
-
- Limbach HH, Seiffert W. Dynamic processes in systems with hydrogen-bonds .2. H-1 NMR spectroscopic investigation of direct and indirect intermolecular proton-exchange of N,N'-dipentadeuterophenyl-1-amino-3-imino-propene in CS2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1974;78:641–647.
-
- Ramsey NF. Magnetic shielding of nuclei in molecules. Phys. Rev. 1950;78:699–703. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.78.699. - DOI
-
- Abragam A. The Principles of Nuclear Magnetism. Oxford: Clarendon Press; 1961.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

