Engineering multi-layered tissue constructs using acoustic levitation
- PMID: 31278312
- PMCID: PMC6611909
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46201-z
Engineering multi-layered tissue constructs using acoustic levitation
Abstract
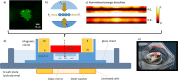
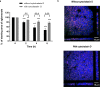
Engineering tissue structures that mimic those found in vivo remains a challenge for modern biology. We demonstrate a new technique for engineering composite structures of cells comprising layers of heterogeneous cell types. An acoustofluidic bioreactor is used to assemble epithelial cells into a sheet-like structure. On transferring these cell sheets to a confluent layer of fibroblasts, the epithelial cells cover the fibroblast surface by collective migration maintaining distinct epithelial and fibroblast cell layers. The collective behaviour of the epithelium is dependent on the formation of cell-cell junctions during levitation and contrasts with the behaviour of mono-dispersed epithelial cells where cell-matrix interactions dominate and hinder formation of discrete cell layers. The multilayered tissue model is shown to form a polarised epithelial barrier and respond to apical challenge. The method is useful for engineering a wide range of layered tissue types and mechanistic studies on collective cell migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Polyelectrolyte nano-scaffolds for the design of layered cellular architectures.Tissue Eng. 2006 Jun;12(6):1553-63. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.12.1553. Tissue Eng. 2006. PMID: 16846351
-
Human stem cell based corneal tissue mimicking structures using laser-assisted 3D bioprinting and functional bioinks.Biomaterials. 2018 Jul;171:57-71. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.04.034. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Biomaterials. 2018. PMID: 29684677
-
2D/3D buccal epithelial cell self-assembling as a tool for cell phenotype maintenance and fabrication of multilayered epithelial linings in vitro.Biomed Mater. 2018 Jul 19;13(5):054104. doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/aace1c. Biomed Mater. 2018. PMID: 29926804
-
Three-dimensional cardiac tissue fabrication based on cell sheet technology.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Jan 15;96:103-9. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.05.002. Epub 2015 May 14. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 25980939 Review.
-
Construction of three-dimensional vascularized cardiac tissue with cell sheet engineering.J Control Release. 2015 May 10;205:83-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.12.016. Epub 2014 Dec 16. J Control Release. 2015. PMID: 25523520 Review.
Cited by
-
The utility of biomedical scaffolds laden with spheroids in various tissue engineering applications.Theranostics. 2021 May 3;11(14):6818-6832. doi: 10.7150/thno.58421. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34093855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-organization and culture of Mesenchymal Stem Cell spheroids in acoustic levitation.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 16;11(1):8355. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87459-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33863936 Free PMC article.
-
The Structure and Function of Next-Generation Gingival Graft Substitutes-A Perspective on Multilayer Electrospun Constructs with Consideration of Vascularization.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 9;23(9):5256. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095256. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The waves that make the pattern: a review on acoustic manipulation in biomedical research.Mater Today Bio. 2021 Mar 24;10:100110. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100110. eCollection 2021 Mar. Mater Today Bio. 2021. PMID: 33997761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coalescence Dynamics of Acoustically Levitated Droplets.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Mar 26;11(4):343. doi: 10.3390/mi11040343. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32224992 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

