An Electrical Model of Hydrocephalus Shunt Incorporating the CSF Dynamics
- PMID: 31278327
- PMCID: PMC6611941
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46328-z
An Electrical Model of Hydrocephalus Shunt Incorporating the CSF Dynamics
Abstract
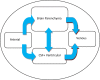
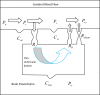
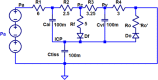
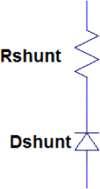
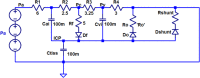
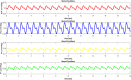
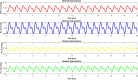
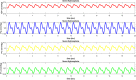
The accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in brain ventricles and subarachnoid space is known as hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus is a result of disturbances in the secretion or absorption process of CSF. A hydrocephalus shunt is an effective method for the treatment of hydrocephalus. In this paper, at first, the procedures of secretion, circulation, and absorption of CSF are studied and subsequently, the mathematical relations governing the pressures in different interacting compartments of the brain are considered. A mechanical-electrical model is suggested based on the brain physiology and blood circulation. In the proposed model, hydrocephalus is modeled with an incremental resistance (Ro) and hydrocephalus shunt, which is a low resistance path to drain the accumulated CSF in the brain ventricles, is modeled with a resistance in series with a diode. At the end, the simulation results are shown. The simulation results can be used to predict the shunt efficiency in reducing CSF pressure and before a real shunt implementation surgery is carried out in a patient's body.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures
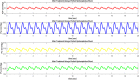
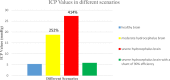
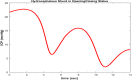
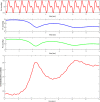
References
-
- Pollay M. Cerebrospinal Fluid in Diseases of the Nervous System. Neurosurgery. 1993;32:325. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199302000-00029. - DOI
-
- Cortex, C. Reference module in neuroscience and biobehavioral psychology (2016).
-
- Wartenberg KE. Update on the management of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Future Neurol. 2013;8:205–224. doi: 10.2217/fnl.13.2. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

