Precision medicine and health disparities: The case of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 31279488
- PMCID: PMC6768085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.outlook.2019.05.003
Precision medicine and health disparities: The case of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
Background: Precision medicine has uncertain potential to address population health disparities.
Purpose: Case study of disparities in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Method: Literature-based evaluation of ALL in African American (AA) and European American (EA) children.
Findings: AA children have a lower incidence of ALL than EA children, experience higher relapse rates, and are more likely to be diagnosed with poor prognostic indicators. Environmental risk exposures for ALL have small effect sizes; data are insufficient to determine their contribution to differences in incidence and prognosis. Differences in prevalence of gene variants associated with treatment response contribute to higher relapse rates in AA children. However, higher relapse rates were not seen in a care setting that eliminated out of pocket costs, used risk-directed therapy, and included rigorous case management.
Discussion: Unequal access to effective treatment contributes to ALL disparities. Precision medicine can help to define effective treatment for diverse patient populations.
Keywords: Childhood leukemia; Health disparities; Pharmacogenomics; Precision medicine.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
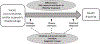
References
-
- Acquati F, Possati L, Ferrante L, Campomenosi P, Talevi S, Bardelli S, et al. Tumor and metastasis suppression by the human RNASET2 gene. Int J Oncol 2005. May;26(5):1159–68. - PubMed
-
- Ashley E Towards precision medicine. Nat Rev Genet 2016;17(9):507–22. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia S Influence of race and socioeconomic status on outcome of children treated for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Curr Opin Pediatr 2004;169:9–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

