Predicting drug-free remission in rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective interventional cohort study
- PMID: 31280933
- PMCID: PMC6891251
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.06.009
Predicting drug-free remission in rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective interventional cohort study
Erratum in
-
Erratum to "Predicting drug-free remission in rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective interventional cohort study" [J. Autoimmun. 105 (December 2019) 102298].J Autoimmun. 2022 Oct;132:102913. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102913. Epub 2022 Sep 20. J Autoimmun. 2022. PMID: 36137863 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Many patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) achieve disease remission with modern treatment strategies. However, having achieved this state, there are no tests that predict when withdrawal of therapy will result in drug-free remission rather than flare. We aimed to identify predictors of drug-free remission in RA.
Methods: The Biomarkers of Remission in Rheumatoid Arthritis (BioRRA) Study was a unique, prospective, interventional cohort study of complete and abrupt cessation of conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Patients with RA of at least 12 months duration and in clinical and ultrasound remission discontinued DMARDs and were monitored for six months. The primary outcome was time-to-flare, defined as disease activity score in 28 joints with C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) ≥ 2.4. Baseline clinical and ultrasound measures, circulating inflammatory biomarkers, and peripheral CD4+ T cell gene expression were assessed for their ability to predict time-to-flare and flare/remission status by Cox regression and receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis respectively.
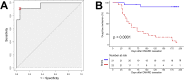
Results: 23/44 (52%) eligible patients experienced an arthritis flare after a median (IQR) of 48 (31.5-86.5) days following DMARD cessation. A composite score incorporating five baseline variables (three transcripts [FAM102B, ENSG00000228010, ENSG00000227070], one cytokine [interleukin-27], one clinical [Boolean remission]) differentiated future flare from drug-free remission with an area under the ROC curve of 0.96 (95% CI 0.91-1.00), sensitivity 0.91 (0.78-1.00) and specificity 0.95 (0.84-1.00).
Conclusion: We provide proof-of-concept evidence for predictors of drug-free remission in RA. If validated, these biomarkers could help to personalize immunosuppressant withdrawal: a therapy paradigm shift with ensuing patient and economic benefits.
Keywords: Biomarker; CD4(+) T cell; Cessation; Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug; Drug-free remission; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Smolen J.S., Landewé R., Bijlsma J., Burmester G., Chatzidionysiou K., Dougados M. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017;76:960. - PubMed
-
- Ledingham J., Gullick N., Irving K., Gorodkin R., Aris M., Burke J. BSR and BHPR guideline for the prescription and monitoring of non-biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Rheumatology. 2017;56:865–868. - PubMed
-
- Singh J.A., Saag K.G., Bridges S.L., Jr., Akl E.A., Bannuru R.R., Sullivan M.C. 2015 American College of rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2016;68:1–26. - PubMed
-
- van der Woude D., Young A., Jayakumar K., Mertens B.J., Toes R.E., van der Heijde D. Prevalence of and predictive factors for sustained disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-free remission in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from two large early arthritis cohorts. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:2262–2271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

