Neuregulin-1β Partially Improves Cardiac Function in Volume-Overload Heart Failure Through Regulation of Abnormal Calcium Handling
- PMID: 31281251
- PMCID: PMC6597678
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00616
Neuregulin-1β Partially Improves Cardiac Function in Volume-Overload Heart Failure Through Regulation of Abnormal Calcium Handling
Abstract
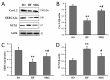
Background: Neuregulin (NRG-1), an essential stress-mediated paracrine growth factor, has a cardioprotective effect in failing heart. However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. The role of NRG-1β in heart failure (HF) rats was examined. Methods and Results: Volume-overload HF rat model was created by aortocaval fistula surgery. The sham-operated (SO) rats received the same surgical intervention without the fistula. Thirty-five HF rats were injected with NRG-1β (NRG, 10 μg/kg·d) via the tail vein for 7 days, whereas 35 HF rats and 20 SO rats were injected with the same dose of saline. The echocardiographic findings showed left ventricular dilatation, systolic and diastolic dysfunction, and QTc interval prolongation in HF rats. The NRG-1β treatment attenuated the ventricular remodeling and shortened the QTc interval. Patch clamp recordings showed ICa-L was significantly decreased in the HF group, and NRG-1β treatment attenuated the decreased ICa-L. No significant differences in the kinetic properties of ICa-L were observed. The expressions of Cav1.2 and SERCA2a were significantly reduced, but the expression level of NCX1 was increased dramatically in the HF group. NRG-1β treatment could partially prevent the decrease of Cav1.2 and SERCA2a, and the increase of NCX1 in HF rats. Conclusions: NRG-1β could partly attenuate the heart function deterioration in the volume-overload model. Reduced function and expression of calcium transportation-related proteins might be the underlying mechanism.
Keywords: L-type calcium channel; SERCA2a; calcium handling; heart failure; neuregulin-1β.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Improvement of cardiac function and reversal of gap junction remodeling by Neuregulin-1β in volume-overloaded rats with heart failure.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2012 Jun;9(2):172-9. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1263.2012.03271. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22916065 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Neuregulin-1β Treatment Mitigates the Progression of Postmyocardial Infarction Heart Failure in the Setting of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus by Suppressing Myocardial Apoptosis, Fibrosis, and Key Oxidant-Producing Enzymes.J Card Fail. 2017 Dec;23(12):887-899. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2017.08.456. Epub 2017 Sep 4. J Card Fail. 2017. PMID: 28870731 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of neuregulin-1 on heart function and inflammatory mediators in rats with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Feb;30(2):140-144. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.02.009. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 29402363 Chinese.
-
Neuregulin as a heart failure therapy and mediator of reverse remodeling.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2014 Mar;11(1):40-9. doi: 10.1007/s11897-013-0176-2. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2014. PMID: 24234399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuregulin-1 and its potential role in the control of cardiac function.Heart Fail Monit. 2008 Feb 1;5(4):119-24. Heart Fail Monit. 2008. PMID: 18273495 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Serum Proteome Profiling of Canine Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia before and after Castration.Animals (Basel). 2023 Dec 14;13(24):3853. doi: 10.3390/ani13243853. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136890 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Trandolapril on Structural, Contractile and Electrophysiological Remodeling in Experimental Volume Overload Heart Failure.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 10;12:729568. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.729568. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34566652 Free PMC article.
-
Neuregulin-1, a potential therapeutic target for cardiac repair.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 31;13:945206. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.945206. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuregulin-1, a member of the epidermal growth factor family, mitigates STING-mediated pyroptosis and necroptosis in ischaemic flaps.Burns Trauma. 2024 Jun 9;12:tkae035. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkae035. eCollection 2024. Burns Trauma. 2024. PMID: 38855574 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Gamma Secretase as a Therapeutic Target for Cardiac Diseases.J Pers Med. 2021 Dec 4;11(12):1294. doi: 10.3390/jpm11121294. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34945766 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fukazawa R., Miller T. A., Kuramochi Y., Frantz S., Kim Y. D., Marchionni M. A., et al. (2003). Neuregulin-1 protects ventricular myocytes from anthracycline-induced apoptosis via erbB4-dependent activation of PI3-kinase/Akt. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 35, 1473–1479. 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2003.09.012 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

