Application of Deep Learning in Neuroradiology: Brain Haemorrhage Classification Using Transfer Learning
- PMID: 31281335
- PMCID: PMC6589279
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/4629859
Application of Deep Learning in Neuroradiology: Brain Haemorrhage Classification Using Transfer Learning
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Application of Deep Learning in Neuroradiology: Brain Haemorrhage Classification Using Transfer Learning".Comput Intell Neurosci. 2020 Aug 28;2020:4705838. doi: 10.1155/2020/4705838. eCollection 2020. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32908475 Free PMC article.
Abstract
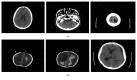
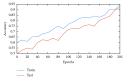
In this paper, we address the problem of identifying brain haemorrhage which is considered as a tedious task for radiologists, especially in the early stages of the haemorrhage. The problem is solved using a deep learning approach where a convolutional neural network (CNN), the well-known AlexNet neural network, and also a modified novel version of AlexNet with support vector machine (AlexNet-SVM) classifier are trained to classify the brain computer tomography (CT) images into haemorrhage or nonhaemorrhage images. The aim of employing the deep learning model is to address the primary question in medical image analysis and classification: can a sufficient fine-tuning of a pretrained model (transfer learning) eliminate the need of building a CNN from scratch? Moreover, this study also aims to investigate the advantages of using SVM as a classifier instead of a three-layer neural network. We apply the same classification task to three deep networks; one is created from scratch, another is a pretrained model that was fine-tuned to the brain CT haemorrhage classification task, and our modified novel AlexNet model which uses the SVM classifier. The three networks were trained using the same number of brain CT images available. The experiments show that the transfer of knowledge from natural images to medical images classification is possible. In addition, our results proved that the proposed modified pretrained model "AlexNet-SVM" can outperform a convolutional neural network created from scratch and the original AlexNet in identifying the brain haemorrhage.
Figures






References
-
- Balasooriya U., Perera M. S. Intelligent brain haemorrhage diagnosis using artificial neural networks. Proceedings of the Business Engineering and Industrial Applications Colloquium (BEIAC); September 2012; Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. IEEE; pp. 128–133.
-
- Morgenstern L. B., Hemphill J. C., Anderson C., et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2010;46:2032–2060. - PubMed
-
- Helwan A., Abiyev R. Shape and texture features for the identification of breast cancer. Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science; October 2016; San Francisco, USA. pp. 19–21.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

