MicroRNA-146a improves sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by regulating the TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 31281454
- PMCID: PMC6591494
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7657
MicroRNA-146a improves sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by regulating the TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
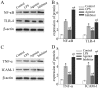
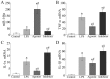
The aim of the current study was to investigate the regulatory effect of miR-146a on the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4)/NF-κB pathway and therefore inflammation in septic cardiomyopathy. A total of 60 healthy male Sprague Dawley rats were equally divided into a control, LPS, miR-146a agonist and miR-146a inhibitor group. Blood samples were collected from rats 24 h after intraperitoneal lipopolysaccharide injection and myocardial tissues were subsequently collected. After hematoxylin and eosin staining of rat myocardial tissues, the degree of inflammatory cell infiltration and myocardial damage was observed. The content of certain myocardial injury markers were also observed, including cardiac troponin I (cTnI), B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), creatine kinase myocardial bound (CK-MB) and myoglobin (Mb). Western blot analysis was performed to detect the expression of NF-κB/TLR-4, tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in myocardial tissues. Reverse transcription-quantitative (RT-q) PCR was used to detect the expression of miR-146a, TNF-α, interleukin (IL)-1α and IL-1β mRNA in myocardial tissues. In the LPS group, myocardial interstitial tissue edema occurred, with enlarged and loosely arranged cardiomyocytes. Compared with the sepsis model group, myocardial interstitial tissue edema was relieved in the miR-146a agonist group, but was aggravated in the miR-146a inhibition group. The serum levels of cTnI, BNP, CK-MB, Mb, NF-κB, TLR-4, TNF-α and ICAM-1 in the sepsis model group were higher than those in the control group. In the miR-146a agonist group, levels of myocardial injury markers were lower than those in the sepsis model group, but were higher in the miR-146a inhibition group. The results of RT-qPCR demonstrated that the expression of miR-146a, TNF-α, IL-1α and IL-1β in the sepsis model group were upregulated compared with the control group. In addition, miR-146a expression in the miR-146a agonist group and the miR-146a inhibition group was increased, but TNF-α, IL-1α and IL-1β mRNA was downregulated. miR-146a may regulate the TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway via negative feedback mechanisms, leading to the improvement of the inflammatory response and cardiac dysfunction in sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: lipopolysaccharide; microRNA-146a; sepsis; toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-κB pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Protective effect of TAK242 blocking Toll-like receptor 4 pathway on septic myocardial injury and cardiac dysfunction].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Oct;33(10):1226-1231. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210620-00915. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 34955133 Chinese.
-
[Protective effects of microRNA-181b on aged rats with sepsis-induced hippocampus injury in vivo].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Jul;31(7):857-861. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.07.012. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31441410 Chinese.
-
MiR-146a mediates TLR-4 signaling pathway to affect myocardial fibrosis in rat constrictive pericarditis model.J Thorac Dis. 2021 Feb;13(2):935-945. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-2716. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 33717566 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of miR-146a: a causative factor in epilepsy pathogenesis, diagnosis, and prognosis.Front Neurol. 2023 May 5;14:1094709. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1094709. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37213914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression Levels of Candidate Circulating microRNAs in Early-Onset Neonatal Sepsis Compared With Healthy Newborns.Genomics Insights. 2018 Sep 2;11:1178631018797079. doi: 10.1177/1178631018797079. eCollection 2018. Genomics Insights. 2018. PMID: 30202206 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress on the Mechanism of Sepsis Induced Myocardial Injury.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Jul 26;15:4275-4290. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S374117. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35923903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current insight on the mechanisms of programmed cell death in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Dec 15;11:1309719. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1309719. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38161332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An engineered miRNA PS-OMe miR130 inhibits acute lung injury by targeting eCIRP in sepsis.Mol Med. 2023 Feb 13;29(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00607-8. Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36782115 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-495 serves as a diagnostic biomarker in patients with sepsis and regulates sepsis-induced inflammation and cardiac dysfunction.Eur J Med Res. 2019 Nov 26;24(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40001-019-0396-3. Eur J Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31771650 Free PMC article.
-
miR-200a-3p Attenuates Coronary Microembolization-Induced Myocardial Injury in Rats by Inhibiting TXNIP/NLRP3-Mediated Cardiomyocyte Pyroptosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Aug 5;8:693257. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.693257. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34422922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tønnesen E, Larsen K. Severe sepsis and septic shock. Ugeskr Laeger. 2014;176:V03130200. (In Danish) - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
