Interactions between antidepressants, sleep aids and selected breast cancer therapy
- PMID: 31281608
- PMCID: PMC6589536
- DOI: 10.4081/mi.2019.8115
Interactions between antidepressants, sleep aids and selected breast cancer therapy
Abstract
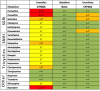
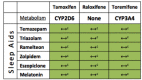
Depression and insomnia are very significant pathologies in cancer patients as they contribute to the patient's overall cure and quality of life. Moreover, untreated depression and ongoing insomnia are associated with decreased immune responses and lower survival rates. With all disease states and especially with cancer, close attention to drug-drug interactions and the potential impact on the efficacy of therapy is paramount. One area of particular interest due to the lack of well-done clinical trials is drug-drug interaction(s) between antidepressants and cancer treatment. Pharmacokinetics of a certain drug allows for prediction of certain drug interactions based on chemical properties of the agents involved. If the agents depend on their metabolites for activity, active drug level will be decreased through this enzyme inhibition. In this paper, we looked at the cytochrome-P450 drug interactions between antidepressants and sleep aids with Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERM). Newer SERM metabolisms are less influenced by interactions with medications used to treat depression. However, tamoxifen metabolism could be severely altered by several antidepressants. This has direct consequences as patients on tamoxifen and antidepressant can have double the risk of relapse to cancer in two years. We discussed those interactions and made recommendations for clinical use.
Keywords: cancer patients; depression; drugs interaction; insomnia.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: the authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74039-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17993229 Review.
-
The Role of Metabolites of Antidepressants in the Treatment of Depression.CNS Drugs. 1997 Apr;7(4):273-312. doi: 10.2165/00023210-199707040-00003. CNS Drugs. 1997. PMID: 27520753 Review.
-
[Antagonism of tamoxifen and antidepressants among women with breast cancer].Rev Med Chil. 2011 Jan;139(1):89-99. Epub 2011 Apr 11. Rev Med Chil. 2011. PMID: 21526323 Review. Spanish.
-
Drug therapy for geriatric depression.Drugs Aging. 1993 May-Jun;3(3):195-219. doi: 10.2165/00002512-199303030-00002. Drugs Aging. 1993. PMID: 8324296 Review.
-
[Clinically relevant drug interactions with new generation antidepressants and antipsychotics].Ther Umsch. 2009 Jun;66(6):485-92. doi: 10.1024/0040-5930.66.6.485. Ther Umsch. 2009. PMID: 19496045 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Association between antidepressant use and second breast cancer event after ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosis: a nested case-control study.Cancer Causes Control. 2022 Apr;33(4):593-600. doi: 10.1007/s10552-021-01551-w. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Cancer Causes Control. 2022. PMID: 35061141
-
Review of Psilocybin Use for Depression among Cancer Patients after Approval in Oregon.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 27;16(9):1702. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091702. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38730654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture and moxibustion for malignant tumor patients with psychological symptoms of insomnia, anxiety and depression: a systematic review and Meta-analysis.J Tradit Chin Med. 2023 Jun;43(3):441-456. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230313.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 37147745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vitali M, Ripamonti CI, Roila F, et al. Cognitive impairment and chemotherapy: a brief overview. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2017;118:7-14. - PubMed
-
- Ren X, St Clair DK, Butterfield DA. Dysregulation of cytokine mediated chemotherapy induced cognitive impairment. Pharmacol Res 2017;117: 267-73. - PubMed
-
- Wardill HR, Mander KA, Van Sebille YZ, et al. Cytokine-mediated blood brain barrier disruption as a conduit for cancer/ chemotherapy-associated neurotoxicity and cognitive dysfunction. Int J Cancer 2016;139:2635-45. - PubMed
-
- Zainal NZ, Nik-Jaafar NR, Baharudin A, et al. Prevalence of depression in breast cancer survivors: a systematic review of observational studies. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2013;14:2649-56. - PubMed

