Single-base mapping of m6A by an antibody-independent method
- PMID: 31281898
- PMCID: PMC6609220
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aax0250
Single-base mapping of m6A by an antibody-independent method
Abstract
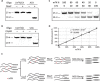
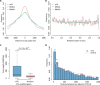
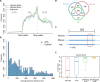
N 6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most abundant messenger RNA modifications in eukaryotes involved in various pivotal processes of RNA metabolism. The most popular high-throughput m6A identification method depends on the anti-m6A antibody but suffers from poor reproducibility and limited resolution. Exact location information is of great value for understanding the dynamics, machinery, and functions of m6A. Here, we developed a precise and high-throughput antibody-independent m6A identification method based on the m6A-sensitive RNA endoribonuclease recognizing ACA motif (m6A-sensitive RNA-Endoribonuclease-Facilitated sequencing or m6A-REF-seq). Whole-transcriptomic, single-base m6A maps generated by m6A-REF-seq quantitatively displayed an explicit distribution pattern with enrichment near stop codons. We used independent methods to validate methylation status and abundance of individual m6A sites, confirming the high reliability and accuracy of m6A-REF-seq. We applied this method on five tissues from human, mouse, and rat, showing that m6A sites are conserved with single-nucleotide specificity and tend to cluster among species.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mapping single-nucleotide m6A by m6A-REF-seq.Methods. 2022 Jul;203:392-398. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2021.06.013. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Methods. 2022. PMID: 34174388
-
Antibody-free enzyme-assisted chemical approach for detection of N6-methyladenosine.Nat Chem Biol. 2020 Aug;16(8):896-903. doi: 10.1038/s41589-020-0525-x. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Nat Chem Biol. 2020. PMID: 32341502
-
Genome-Wide Location Analyses of N6-Methyladenosine Modifications (m6A-Seq).Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1562:45-53. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6807-7_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28349453 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping N6 -Methyladenosine (m6 A) in RNA: Established Methods, Remaining Challenges, and Emerging Approaches.Chemistry. 2019 Mar 7;25(14):3455-3464. doi: 10.1002/chem.201804043. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Chemistry. 2019. PMID: 30347476 Review.
-
Advances in the profiling of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications.Biotechnol Adv. 2020 Dec;45:107656. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2020.107656. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Biotechnol Adv. 2020. PMID: 33181242 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel insight into the functions of N6‑methyladenosine modified lncRNAs in cancers (Review).Int J Oncol. 2022 Dec;61(6):152. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5442. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Int J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36263625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative and single nucleotide RNA m6 A detection technology boosts clinical research based on tissue and cell free RNA modification.Clin Transl Med. 2022 Oct;12(10):e1082. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1082. Clin Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36263692 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
DirectRMDB: a database of post-transcriptional RNA modifications unveiled from direct RNA sequencing technology.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D106-D116. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1061. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36382409 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of bacterial transcriptome and epitranscriptome using nanopore direct RNA sequencing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 27;52(15):8746-8762. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae601. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39011882 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating the pitfalls of mapping DNA and RNA modifications.Nat Rev Genet. 2023 Jun;24(6):363-381. doi: 10.1038/s41576-022-00559-5. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Nat Rev Genet. 2023. PMID: 36653550 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fu Y., Dominissini D., Rechavi G., He C., Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m6A RNA methylation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 15, 293–306 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Barbieri I., Tzelepis K., Pandolfini L., Shi J., Millán-Zambrano G., Robson S. C., Aspris D., Migliori V., Bannister A. J., Han N., De Braekeleer E., Ponstingl H., Hendrick A., Vakoc C. R., Vassiliou G. S., Kouzarides T., Promoter-bound METTL3 maintains myeloid leukaemia by m6A-dependent translation control. Nature 552, 126–131 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Batista P. J., Molinie B., Wang J., Qu K., Zhang J., Li L., Bouley D. M., Lujan E., Haddad B., Daneshvar K., Carter A. C., Flynn R. A., Zhou C., Lim K.-S., Dedon P., Wernig M., Mullen A. C., Xing Y., Giallourakis C. C., Chang H. Y., m6A RNA modification controls cell fate transition in mammalian embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 15, 707–719 (2014). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gokhale N. S., McIntyre A. B. R., McFadden M. J., Roder A. E., Kennedy E. M., Gandara J. A., Hopcraft S. E., Quicke K. M., Vazquez C., Willer J., Ilkayeva O. R., Law B. A., Holley C. L., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Evans M. J., Suthar M. S., Bradrick S. S., Mason C. E., Horne S. M., N6-Methyladenosine in Flaviviridae Viral RNA Genomes Regulates Infection. Cell Host Microbe 20, 654–665 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lence T., Akhtar J., Bayer M., Schmid K., Spindler L., Ho C. H., Kreim N., Andrade-Navarro M. A., Poeck B., Helm M., Roignant J.-Y., m6A modulates neuronal functions and sex determination in Drosophila. Nature 540, 242–247 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

