TxtH is a key component of the thaxtomin biosynthetic machinery in the potato common scab pathogen Streptomyces scabies
- PMID: 31282068
- PMCID: PMC6792134
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.12843
TxtH is a key component of the thaxtomin biosynthetic machinery in the potato common scab pathogen Streptomyces scabies
Abstract
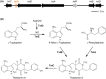
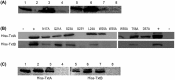
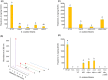
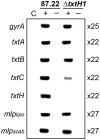
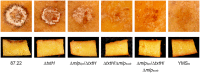
Streptomyces scabies causes potato common scab disease, which reduces the quality and market value of affected tubers. The predominant pathogenicity determinant produced by S. scabies is the thaxtomin A phytotoxin, which is essential for common scab disease development. Production of thaxtomin A involves the nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) TxtA and TxtB, both of which contain an adenylation (A-) domain for selecting and activating the appropriate amino acid during thaxtomin biosynthesis. The genome of S. scabies 87.22 contains three small MbtH-like protein (MLP)-coding genes, one of which (txtH) is present in the thaxtomin biosynthesis gene cluster. MLP family members are typically required for the proper folding of NRPS A-domains and/or stimulating their activities. This study investigated the importance of TxtH during thaxtomin biosynthesis in S. scabies. Biochemical studies showed that TxtH is required for promoting the soluble expression of both the TxtA and TxtB A-domains in Escherichia coli, and amino acid residues essential for this activity were identified. Deletion of txtH in S. scabies significantly reduced thaxtomin A production, and deletion of one of the two additional MLP homologues in S. scabies completely abolished production. Engineered expression of all three S. scabies MLPs could restore thaxtomin A production in a triple MLP-deficient strain, while engineered expression of MLPs from other Streptomyces spp. could not. Furthermore, the constructed MLP mutants were reduced in virulence compared to wild-type S. scabies. The results of our study confirm that TxtH plays a key role in thaxtomin A biosynthesis and plant pathogenicity in S. scabies.
Keywords: Streptomyces scabies; MbtH-like protein; adenylation domain; nonribosomal peptide synthetases; potato common scab; thaxtomin A.
© 2019 The Authors. Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional Cross-Talk of MbtH-Like Proteins During Thaxtomin Biosynthesis in the Potato Common Scab Pathogen Streptomyces scabiei.Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 15;11:585456. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.585456. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33178168 Free PMC article.
-
Thaxtomin biosynthesis: the path to plant pathogenicity in the genus Streptomyces.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2008 Jun;94(1):3-10. doi: 10.1007/s10482-008-9240-4. Epub 2008 Apr 5. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2008. PMID: 18392685
-
Thaxtomin A production and virulence are controlled by several bld gene global regulators in Streptomyces scabies.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2014 Aug;27(8):875-85. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-02-14-0037-R. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2014. PMID: 24678834
-
Genetic and physiological determinants of Streptomyces scabies pathogenicity.Mol Plant Pathol. 2009 Sep;10(5):579-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00561.x. Mol Plant Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19694949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of virulence mechanisms in plant-pathogenic Streptomyces.Can J Microbiol. 2024 Jun 1;70(6):199-212. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2023-0171. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Can J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38190652 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural and engineered cyclodipeptides: Biosynthesis, chemical diversity, and engineering strategies for diversification and high-yield bioproduction.Eng Microbiol. 2022 Dec 24;3(1):100067. doi: 10.1016/j.engmic.2022.100067. eCollection 2023 Mar. Eng Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 39628525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Cross-Talk of MbtH-Like Proteins During Thaxtomin Biosynthesis in the Potato Common Scab Pathogen Streptomyces scabiei.Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 15;11:585456. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.585456. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33178168 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics of the niche-specific plant pathogen Streptomyces ipomoeae reveal novel genome content and organization.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Dec 21;89(12):e0030823. doi: 10.1128/aem.00308-23. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38009923 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Genetic Architecture for Common Scab (Streptomyces scabei L.) Resistance in Diploid Potatoes.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 28;26(3):1126. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031126. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940897 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomics reveals insight into the phylogeny and habitat adaptation of novel Amycolatopsis species, an endophytic actinomycete associated with scab lesions on potato tubers.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Mar 27;15:1346574. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1346574. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38601305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baltz, R.H. (2011) Function of MbtH homologs in nonribosomal peptide biosynthesis and applications in secondary metabolite discovery. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38, 1747–1760. - PubMed
-
- Bignell, D.R.D. , Huguet‐Tapia, J.C. , Joshi, M.V. , Pettis, G.S. and Loria, R. (2010a) What does it take to be a plant pathogen: genomic insights from Streptomyces species. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 98, 179–194. - PubMed
-
- Bignell, D.R.D. , Seipke, R.F. , Huguet‐Tapia, J.C. , Chambers, A.H. , Parry, R.J. and Loria, R. (2010b) Streptomyces scabies 87–22 contains a coronafacic acid‐like biosynthetic cluster that contributes to plant‐microbe interactions. Mol. Plant‐Microbe Interact. 23, 161–175. - PubMed
-
- Bignell, D.R.D. , Fyans, J.K. and Cheng, Z. (2014) Phytotoxins produced by plant pathogenic Streptomyces species. J. Appl. Microbiol. 116, 223–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

