Impact of water hardness on oxytetracycline oral bioavailability in fed and fasted piglets
- PMID: 31282118
- PMCID: PMC6868454
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.185
Impact of water hardness on oxytetracycline oral bioavailability in fed and fasted piglets
Abstract
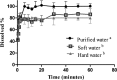
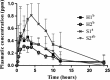
Water hardness is a critical factor that affects oxytetracycline dissolution by chelation with cations. These interactions may lead to impaired dosing and consequently decrease absorption. Moreover, feed present in gastrointestinal tract may interact with antibiotic and alter pharmacokinetic parameters. In the present study, dissolution profiles of an oxytetracycline veterinary formulation were assessed in purified, soft and hard water. Furthermore, oxytetracycline absolute bioavailability, after oral administration of the drug dissolved in soft or hard water, was evaluated in fed and fasted piglets. A maximum dissolution of 86% and 80% was obtained in soft and hard water, respectively, while in purified water dissolution was complete. Results from in vivo study reconfirmed oxytetracycline's very low oral bioavailability. The greatest values were attained when antibiotic was dissolved in soft water and in fasted animals. Statistically significant lower absolute bioavailability was achieved when hard water was used and/or animals were fed. Moreover, Cmax attained in all treatments was lower than MIC90 of most important swine pathogens. For these reasons, the oral use of OTC formulations, that have demonstrated low oral bioavailability, should be avoided to treat systemic diseases in pigs.
Keywords: bioavailability; oxytetracycline; piglets; water hardness.
© 2019 The Authors. Veterinary Medicine and Science Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The vehicle of administration, feed or water, and prandial state influence the oral bioavailability of amoxicillin in piglets.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Aug;48(4):2135-2144. doi: 10.1007/s11259-024-10378-0. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38630426
-
Potential interactions between an oral fosfomycin formulation and feed or drinking water: Impact on bioavailability in piglets.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Sep;44(5):783-792. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12966. Epub 2021 Mar 15. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33720436
-
The Vehicle of Administration and Prandial State May Reduce the Spectrum of Oral Broad-Spectrum Antibiotics (Oxytetracycline, Fosfomycin and Amoxicillin) Administered to Piglets: A Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Approach.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2025 Jan;48(1):37-43. doi: 10.1111/jvp.13479. Epub 2024 Aug 30. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39212299
-
Hard water may increase the inhibitory effect of feed on the oral bioavailability of oxytetracycline in broiler chickens.Pol J Vet Sci. 2019 Jun;22(2):251-258. doi: 10.24425/pjvs.2019.127093. Pol J Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 31269331
-
Bioavailability of oxytetracycline, tetracycline and chlortetracycline after oral administration to fed and fasted pigs.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1996 Aug;19(4):305-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.1996.tb00054.x. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1996. PMID: 8866460
Cited by
-
Removal of antimicrobial prophylaxis and its effect on swine carriage of antimicrobial-resistant coliforms.Sci Prog. 2021 Oct;104(4):368504211050279. doi: 10.1177/00368504211050279. Sci Prog. 2021. PMID: 34872396 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of feed intake and water hardness on fluralaner pharmacokinetics in layer chickens.J Vet Sci. 2022 Sep;23(5):e64. doi: 10.4142/jvs.22048. Epub 2022 Jul 14. J Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36038185 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitudes and practices of government animal health workers on antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance in Timor-Leste.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Nov 24;9:1063530. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1063530. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36504868 Free PMC article.
-
Balantidium Coli in Pig Farms Suspected of Porcine Circovirus Type 2 (PCV2) Associated Enteritis.J Vet Res. 2021 Oct 26;65(4):425-430. doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2021-0057. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 35111995 Free PMC article.
-
The vehicle of administration, feed or water, and prandial state influence the oral bioavailability of amoxicillin in piglets.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Aug;48(4):2135-2144. doi: 10.1007/s11259-024-10378-0. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38630426
References
-
- Bagheri Gh, A. (2015). Thermodynamic studies of metal complexes of tetracycline and its application in drug analysis. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, 48(11), 767–771. 10.1007/s11094-015-1190-3 - DOI
-
- Bagley, C. V. , Kotuby‐Amacher, J. , & Farrel‐Poe, K . (1997). Analysis of water quality for livestock. Utah State University Extension.
-
- Bavera, G. A . (2001). Manual de aguas y aguadas para el ganado.
-
- Brion, M. , Berthon, G. , & Fourtillan, J. B. (1981). Metal ion‐tetracyclines interactions in biological fluids. Potentiometric study of calcium complexes with tetracycline, oxytetracycline, doxycycline and minocycline and simulation of their distributions under physiological conditions. Inorganica Chimica Acta, 55, 47–56. 10.1016/S0020-1693(00)90781-3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

