Regulation of Viral Infection by the RNA Modification N6-Methyladenosine
- PMID: 31283446
- PMCID: PMC6884077
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-virology-092818-015559
Regulation of Viral Infection by the RNA Modification N6-Methyladenosine
Abstract
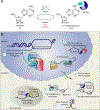
In recent years, the RNA modification N6-methyladenosine (m6A) has been found to play a role in the life cycles of numerous viruses and also in the cellular response to viral infection. m6A has emerged as a regulator of many fundamental aspects of RNA biology. Here, we highlight recent advances in techniques for the study of m6A, as well as advances in our understanding of the cellular machinery that controls the addition, removal, recognition, and functions of m6A. We then summarize the many newly discovered roles of m6A during viral infection, including how it regulates innate and adaptive immune responses to infection. Overall, the goals of this review are to summarize the roles of m6A on both cellular and viral RNAs and to describe future directions for uncovering new functions of m6A during infection.
Keywords: DNA viruses; N6-methyladenosine; RNA modifications; RNA viruses; innate immunity; m6A; post-transcriptional regulation.
Figures
References
-
- Carpenter S, Ricci EP, Mercier BC, Moore MJ, Fitzgerald KA. 2014. Post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol 14:361–76 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

