Decreased expression of gap junction delta-2 (GJD2) messenger RNA and connexin 36 protein in form-deprivation myopia of guinea pigs
- PMID: 31283648
- PMCID: PMC6759107
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000319
Decreased expression of gap junction delta-2 (GJD2) messenger RNA and connexin 36 protein in form-deprivation myopia of guinea pigs
Abstract
Background: More than ten genome-wide association studies have identified the significant association between the gap junction delta-2 (GJD2) gene and myopia. However, no functional studies have been performed to confirm that this gene is correlated with myopia. This study aimed to observe how this gene changed in mRNA and protein level in the form-deprivation myopia (FDM) animal model.
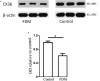
Methods: Four-week-old guinea pigs were randomly divided into two groups: control and FDM groups (n = 12 for each group). The right eyes of the FDM group were covered with opaque hemispherical plastic lenses for 3 weeks. For all the animals, refractive status, axial length (AL), and corneal radius of curvature were measured at baseline and 3 weeks later by streak retinoscope, A-scan ultrasonography, and keratometer, respectively. Retinal GJD2 mRNA expression and connexin 36 (Cx36) levels in FDM and control groups were measured by quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot analyses, respectively. Those results were compared using independent t test, Mann-Whitney U test, or paired t test. A significance level of P < 0.05 was used.
Results: Three weeks later, the FDM group (form-deprived eyes) showed about a myopic shift of approximately -6.75 (-7.94 to -6.31) D, while the control group remained hyperopic with only a shift of -0.50 (-0.75 to 0.25) D (Z = -3.38, P < 0.01). The AL increased by 0.74 (0.61-0.76) and 0.10 (0.05-0.21) mm in FDM and control groups, respectively (Z = -3.37, P < 0.01). The relative mRNA expression of GJD2 in the FDM group decreased 31.58% more than the control group (t = 11.44, P < 0.01). The relative protein expression of CX36 on the retina was lowered by 37.72% in form-deprivation eyes as compared to the controls (t = 17.74, P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Both the mRNA expression of GJD2 and Cx36 protein amount were significantly decreased in the retina of FDM guinea pigs. This indicates that Cx36 is involved in FDM development, providing compensating evidence for the results obtained from genome-wide association studies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Altered Expression of GJD2 Messenger RNA and the Coded Protein Connexin 36 in Negative Lens-induced Myopia of Guinea Pigs.Optom Vis Sci. 2020 Dec;97(12):1080-1088. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000001611. Optom Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 33278187 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Retinal Connexins Cx36 and Horizontal Cell Coupling in Emmetropization in Guinea Pigs.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Jul 1;62(9):27. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.9.27. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34283211 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Constant Flickering Light on Refractive Status, 5-HT and 5-HT2A Receptor in Guinea Pigs.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 13;11(12):e0167902. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167902. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27959948 Free PMC article.
-
Myopia induced by flickering light in guinea pig eyes is associated with increased rather than decreased dopamine release.Mol Vis. 2017 Sep 29;23:666-679. eCollection 2017. Mol Vis. 2017. PMID: 28966549 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of GJD2(Cx36) in Refractive Error Development.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Mar 2;63(3):5. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.3.5. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35262731 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IMI 2021 Yearly Digest.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Apr 28;62(5):7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.5.7. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33909031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Expression of GJD2 Messenger RNA and the Coded Protein Connexin 36 in Negative Lens-induced Myopia of Guinea Pigs.Optom Vis Sci. 2020 Dec;97(12):1080-1088. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000001611. Optom Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 33278187 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of computer-generated patterns with different temporal and spatial frequencies on choroidal thickness, retinal dopamine and candidate genes in chickens wearing lenses.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 10;11:1469275. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1469275. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39720655 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Retinal Connexins Cx36 and Horizontal Cell Coupling in Emmetropization in Guinea Pigs.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Jul 1;62(9):27. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.9.27. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34283211 Free PMC article.
-
Association of CX36 Protein Encoding Gene GJD2 with Refractive Errors.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jun 28;13(7):1166. doi: 10.3390/genes13071166. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35885949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourne RR, Stevens GA, White RA, Smith JL, Flaxman SR, Price H, et al. Causes of vision loss worldwide, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health 2013; 1:e339–e349. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70113-X. - PubMed
-
- Holden BA, Fricke TR, Wilson DA, Jong M, Naidoo KS, Sankaridurg P, et al. Vision Loss Expert Group Global prevalence of myopia and high myopia and temporal trends from 2000 through 2050. Ophthalmology 2016; 123:1036–1042. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2016.01.006. - PubMed
-
- Pan CW, Dirani M, Cheng CY, Wong TY, Saw SM. The age-specific prevalence of myopia in Asia: a meta-analysis. Optom Vis Sci 2015; 92:258–266. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000516. - PubMed
-
- Fricke TR, Jong M, Naidoo KS, Sankaridurg P, Naduvilath TJ, Ho SM, et al. Global prevalence of visual impairment associated with myopic macular degeneration and temporal trends from 2000 through 2050: systematic review, meta-analysis and modelling. Br J Ophthalmol 2018; 102:855–862. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2017-311266. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

