Predicting provenance of forensic soil samples: Linking soil to ecological habitats by metabarcoding and supervised classification
- PMID: 31283764
- PMCID: PMC6613677
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202844
Predicting provenance of forensic soil samples: Linking soil to ecological habitats by metabarcoding and supervised classification
Abstract
Environmental DNA (eDNA) is increasingly applied in ecological studies, including studies with the primary purpose of criminal investigation, in which eDNA from soil can be used to pair samples or reveal sample provenance. We collected soil eDNA samples as part of a large national biodiversity research project across 130 sites in Denmark. We investigated the potential for soil eDNA metabarcoding in predicting provenance in terms of environmental conditions, habitat type and geographic regions. We used linear regression for predicting environmental gradients of light, soil moisture, pH and nutrient status (represented by Ellenberg Indicator Values, EIVs) and Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (QDA) to predict habitat type and geographic region. eDNA data performed relatively well as a predictor of environmental gradients (R2 > 0.81). Its ability to discriminate between habitat types was variable, with high accuracy for certain forest types and low accuracy for heathland, which was poorly predicted. Geographic region was also less accurately predicted by eDNA. We demonstrated the application of provenance prediction in forensic science by evaluating and discussing two mock crime scenes. Here, we listed the plant species from annotated sequences, which can further aid in identifying the likely habitat or, in case of rare species, a geographic region. Predictions of environmental gradients and habitat types together give an overall accurate description of a crime scene, but care should be taken when interpreting annotated sequences, e.g. due to erroneous assignments in GenBank. Our approach demonstrates that important habitat properties can be derived from soil eDNA, and exemplifies a range of potential applications of eDNA in forensic ecology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
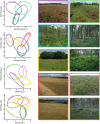
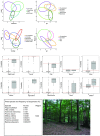
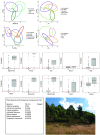
References
-
- Devictor V, van Swaay C, Brereton T, Brotons L, Chamberlain D, Heliölä J, et al. Differences in the climatic debts of birds and butterflies at a continental scale. Nature Climate Change. 2012;2:121 10.1038/nclimate1347 https://www.nature.com/articles/nclimate1347#supplementary-information. - DOI
-
- Parmesan C, Yohe G. A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature. 2003;421:37 10.1038/nature01286 https://www.nature.com/articles/nature01286#supplementary-information. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wiltshire PE. Forensic ecology, botany, and palynology: some aspects of their role in criminal investigation Criminal and environmental soil forensics: Springer; 2009. p. 129–49.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

