Gene-based analysis in HRC imputed genome wide association data identifies three novel genes for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 31283791
- PMCID: PMC6613773
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218111
Gene-based analysis in HRC imputed genome wide association data identifies three novel genes for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
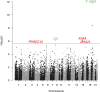
Late onset Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia for which about 30 susceptibility loci have been reported. The aim of the current study is to identify novel genes associated with Alzheimer's disease using the largest up-to-date reference single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) panel, the most accurate imputation software and a novel gene-based analysis approach which tests for patterns of association within genes, in the powerful genome-wide association dataset of the International Genomics of Alzheimer's Project Consortium, comprising over 7 million genotypes from 17,008 Alzheimer's cases and 37,154 controls. In addition to earlier reported genes, we detected three novel gene-wide significant loci PPARGC1A (p = 2.2 × 10-6), RORA (p = 7.4 × 10-7) and ZNF423 (p = 2.1 × 10-6). PPARGC1A and RORA are involved in circadian rhythm; circadian disturbances are one of the earliest symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. PPARGC1A is additionally linked to energy metabolism and the generation of amyloid beta plaques. RORA is involved in a variety of functions apart from circadian rhythm, such as cholesterol metabolism and inflammation. The ZNF423 gene resides in an Alzheimer's disease-specific protein network and is likely involved with centrosomes and DNA damage repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/K013041/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G1100540/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U123160651/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L501517/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0502157/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L023784/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400074/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M009076/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600237/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0901254/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG049505/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L501542/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K01417X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_00024/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1001253/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0300429/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G-1307/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_1604/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0902227/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0900652/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17112/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/J004758/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L023784/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L010305/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases