Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapies for Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 31283897
- PMCID: PMC7427431
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-070918-050501
Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapies for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
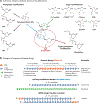
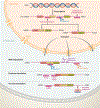
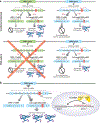
Antisense oligonucleotides represent a novel therapeutic platform for the discovery of medicines that have the potential to treat most neurodegenerative diseases. Antisense drugs are currently in development for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Huntington's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, and multiple research programs are underway for additional neurodegenerative diseases. One antisense drug, nusinersen, has been approved for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy. Importantly, nusinersen improves disease symptoms when administered to symptomatic patients rather than just slowing the progression of the disease. In addition to the benefit to spinal muscular atrophy patients, there are discoveries from nusinersen that can be applied to other neurological diseases, including method of delivery, doses, tolerability of intrathecally delivered antisense drugs, and the biodistribution of intrathecal dosed antisense drugs. Based in part on the early success of nusinersen, antisense drugs hold great promise as a therapeutic platform for the treatment of neurological diseases.
Keywords: Huntington's disease; RNA; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; antisense oligonucleotides; spinal muscular atrophy.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen PM, Al-Chalabi A. 2011. Clinical genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: What do we really know? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 7:603–15 - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Farr SA, Butt W, Kumar VB, Franko MW, Morley JE. 2001. Delivery across the blood-brain barrier of antisense directed against amyloid β: reversal of learning and memory deficits in mice overexpressing amyloid precursor protein. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 297:1113–21 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

