Blockade of L-type Ca2+ channel attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy via suppression of CaMKII-NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 31285514
- PMCID: PMC6614470
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46367-6
Blockade of L-type Ca2+ channel attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy via suppression of CaMKII-NF-κB pathway
Abstract
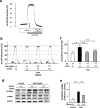
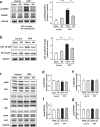
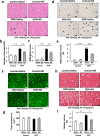
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) play crucial roles in pathogenesis of doxorubicin (DOX)-induced cardiomyopathy. Their activities are regulated by intracellular Ca2+. We hypothesized that blockade of L-type Ca2+ channel (LTCC) could attenuate DOX-induced cardiomyopathy by regulating CaMKII and NF-κB. DOX activated CaMKII and NF-κB through their phosphorylation and increased cleaved caspase 3 in cardiomyocytes. Pharmacological blockade or gene knockdown of LTCC by nifedipine or small interfering RNA, respectively, suppressed DOX-induced phosphorylation of CaMKII and NF-κB and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes, accompanied by decreasing intracellular Ca2+ concentration. Autocamtide 2-related inhibitory peptide (AIP), a selective CaMKII inhibitor, inhibited DOX-induced phosphorylation of NF-κB and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Inhibition of NF-κB activity by ammonium pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate (PDTC) suppressed DOX-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. DOX-treatment (18 mg/kg via intravenous 3 injections over 1 week) increased phosphorylation of CaMKII and NF-κB in mouse hearts. Nifedipine (10 mg/kg/day) significantly suppressed DOX-induced phosphorylation of CaMKII and NF-κB and cardiomyocyte injury and apoptosis in mouse hearts. Moreover, it attenuated DOX-induced left ventricular dysfunction and dilatation. Our findings suggest that blockade of LTCC attenuates DOX-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via suppressing intracellular Ca2+ elevation and activation of CaMKII-NF-κB pathway. LTCC blockers might be potential therapeutic agents against DOX-induced cardiomyopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
β₁-adrenoceptor stimulation promotes LPS-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis through activating PKA and enhancing CaMKII and IκBα phosphorylation.Crit Care. 2015 Mar 9;19(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0820-1. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 25887954 Free PMC article.
-
CaMKII-dependent SR Ca leak contributes to doxorubicin-induced impaired Ca handling in isolated cardiac myocytes.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011 Nov;51(5):749-59. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.07.016. Epub 2011 Jul 26. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21819992 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase mediates the intracellular signalling pathways of cardiac apoptosis in mice with impaired glucose tolerance.J Physiol. 2017 Jun 15;595(12):4089-4108. doi: 10.1113/JP273714. Epub 2017 Mar 2. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28105734 Free PMC article.
-
Is CaMKII a link between inflammation and hypertrophy in heart?J Mol Med (Berl). 2011 Jun;89(6):537-43. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0727-5. Epub 2011 Jan 29. J Mol Med (Berl). 2011. PMID: 21279501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CaMKII, an emerging molecular driver for calcium homeostasis, arrhythmias, and cardiac dysfunction.J Mol Med (Berl). 2007 Jan;85(1):5-14. doi: 10.1007/s00109-006-0125-6. Epub 2006 Nov 21. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17119905 Review.
Cited by
-
Amlodipine alleviates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats through gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) enzyme inhibition, associated with regulation of Nrf2/HO-1, MAPK/NF-κB, and Bax/Bcl-2 signaling.Saudi Pharm J. 2020 Nov;28(11):1317-1325. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.08.022. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Saudi Pharm J. 2020. PMID: 33250641 Free PMC article.
-
Dibenzazepine, a γ-Secretase Enzyme Inhibitor, Protects Against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Suppressing NF-κB, iNOS, and Hes1/Hey1 Expression.Inflammation. 2025 Apr;48(2):557-574. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02046-x. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39078585
-
Advances in research on the correlation between LTCCBs and cardiovascular diseases: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 20;104(25):e42799. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042799. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40550092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IFN-γ-STAT1-ERK Pathway Mediates Protective Effects of Invariant Natural Killer T Cells Against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyocyte Death.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2023 Jun 21;8(8):992-1007. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.02.014. eCollection 2023 Aug. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37719427 Free PMC article.
-
Role of RIPK3‑CaMKII‑mPTP signaling pathway‑mediated necroptosis in cardiovascular diseases (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Oct;52(4):98. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5301. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37654208 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

