Molecular docking and pharmacokinetic evaluation of natural compounds as targeted inhibitors against Crz1 protein in Rhizoctonia solani
- PMID: 31285645
- PMCID: PMC6599437
- DOI: 10.6026/97320630015277
Molecular docking and pharmacokinetic evaluation of natural compounds as targeted inhibitors against Crz1 protein in Rhizoctonia solani
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Molecular docking and pharmacokinetic evaluation of natural compounds as targeted inhibitors against Crz1 protein in Rhizoctonia solani.Bioinformation. 2021 Jun 30;17(6):660. doi: 10.6026/97320630017660. eCollection 2021. Bioinformation. 2021. PMID: 35173389 Free PMC article.
Abstract
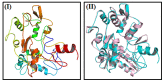
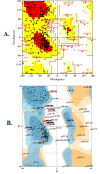
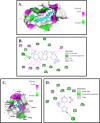
Crz1p regulates Calcineurin, a serine-threonine-specific protein phosphatase, in Rhizoctonia solani. It has attracted consideration as a novel target of antifungal therapy based on studies in numerous pathogenic fungi, including, Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. To investigate whether Calcineurin can be a useful target for the treatment of Crz1 protein in R. solani causing wet root rot in Chickpea. The work presented here reports the in-silico studies of Crz1 protein against natural compounds. This study Comprises of quantitative structure-toxicity relationship (QSTR) and quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR). All compounds showed high binding energy for Crz1 protein through molecular docking. Further, a pharmacokinetic study revealed that these compounds had minimal side effects. Biological activity spectrum prediction of these compounds showed potential antifungal properties by showing significant interaction with Crz1. Hence, these compounds can be used for the prevention and treatment of wet root rot in Chickpea.
Keywords: Crz1; QSAR; QSTR; chickpea; pharmacokinetic.
Figures

References
-
- Aramburu J, et al. Current topics in Cellular Regulation. . 2001;237 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
