Effects of probiotic administration on IGA and IL-6 level in severe burn patients: a randomized trial
- PMID: 31285738
- PMCID: PMC6588324
Effects of probiotic administration on IGA and IL-6 level in severe burn patients: a randomized trial
Abstract
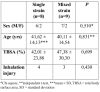
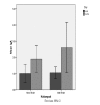
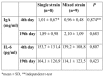
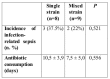
Severe burn injuries are associated with systemic inflammation or even sepsis. A beneficial effect of probiotics on burn patients is reported by regulating the function of the intestinal barrier and reducing inflammation. Immunoglobulin A (IgA) acts as an anti-inflammation antibody, and interleukin 6 (IL-6) as a pro-inflammatory mediator, released extensively in burns. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of single and mixed strain probiotics on the level of IgA and IL-6 in severe burn patients. A randomized double-blind trial was conducted in the burn centre of the Dr. Soetomo Hospital. Severe burn patients with more than 20% total body surface area burned were randomized into two groups. Group one received a single strain and the second group received mixed strain probiotics, once daily for fourteen days. Serum levels of IgA and IL-6 were measured on day 4 post burn injury (before treatment) and day 19 (after treatment). Seventeen burn patients were enrolled in this study. IgA increased significantly from 1.01±0.67 to 1.89±0.98 mg/mL (p<0.001) in the single strain group, and 0.96±0.48 to 2.10±1.09 mg/mL (p=0.025) in the mixed strain group by paired t-test. There was no significant decrease in IL-6 in either group. No significant differences between the two groups were observed for IgA or IL-6. Administration of single and mixed strain probiotics increased IgA level, while there was no decrease in IL-6 level.
Les patients sévèrement brûlés développent SIRS et sepsis. Un effet positif des probiotiques chez ces patients a été évoqué. Il repose sur la régulation de la barrière intestinale et sur un effet anti inflammatoire. IgA est anti inflammatoire, IL-6, secrétée en très grande quantité chez le brûlé, comme pro inflammatoire. Le but de cette étude randomisée en double aveugle réalisée dans le CTB de l’hôpital Dr Soetomo était d’évaluer l’effet de probiotiques (1 ou plusieurs souches) sur les taux d’IgA et d’IL-6 de 17 patients gravement brûlés (> 20% SCT). Le groupe G1 recevait une seule souche de probiotique, le groupe G2 un mélange de souches, 1 fois par jour pendant 2 semaines. Les taux d’IgA et d’IL-6 étaient mesurés à J4 post-brûlure (avant traitement) et à J19 (après traitement). Les 2 groupes étaient statistiquement comparables. L’augmentation d’IgA était significative dans les 2 groupes : 1,01 +/- 0,67 puis 1,89 +/- 0,98 ; p< 0,001 dans le groupe G1 ; 0,98 +/- 0,48 puis 2,1 +/- 1,09 ; p=0,25 dans le groupe G2. Les variations d’IL6 n’étaient pas significatives. Donc l’administration de 1 ou plusieurs souches de probiotiques augmente les taux d’IgA et ne diminue pas ceux d’IL6.
Keywords: Interleukin-6; burn injury; immunoglobulin A; probiotics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Changes in serum contents of interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 and their relation with occurrence of sepsis and prognosis of severely burned patients].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;28(2):111-5. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22781322 Chinese.
-
[Clinical randomized controlled trial on influence of recombinant human growth hormone on the immune function of younger children with severe burn injuries].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2019 Oct 20;35(10):726-732. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2019.10.005. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31658543 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Deficient transforming growth factor beta and interleukin-10 responses contribute to the septic death of burned patients.Burns. 2002 Nov;28(7):631-7. doi: 10.1016/s0305-4179(02)00113-4. Burns. 2002. PMID: 12417156
-
[Influences of hydrogen-rich saline on acute kidney injury in severely burned rats and mechanism].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018 Sep 20;34(9):629-636. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2018.09.013. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30293367 Chinese.
-
Effects Of Oxandrolone On Lean Body Mass (Lbm) In Severe Burn Patients: A Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2022 Mar 31;35(1):55-61. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2022. PMID: 35582088 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics on Wound Infection: A Systematic Review.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025;26(9):1375-1391. doi: 10.2174/0113892010279946240507115337. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38818910
-
Production of electricity and reduction of high-fat diet-induced IL-6 by glucose fermentation of Leuconostoc mesenteroides.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Dec 17;533(4):651-656. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.105. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 33008603 Free PMC article.
-
Accounting for the health risk of probiotics.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 10;10(6):e27908. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27908. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38510031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Off-Label" Medicine Use In Burned Children: Three-Year Retrospective Study.Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2021 Mar 31;34(1):18-25. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2021. PMID: 34054383 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics in Wound Healing.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 24;25(11):5723. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115723. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891909 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(16):1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Belcher HJR. Churchill Livingstone. New York: 1996. Principles and practice of burns management; pp. 163–176.
-
- Jeschke MG, Kamolz LP, Shahrokhi S. Burn Care and Treatment. Springer-Verlag; Wien: 2013. Pathophysiology of burn injury; pp. 415–440.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
