Astrocytic connexin 43 potentiates myelin injury in ischemic white matter disease
- PMID: 31285774
- PMCID: PMC6599652
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.31942
Astrocytic connexin 43 potentiates myelin injury in ischemic white matter disease
Abstract
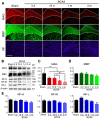
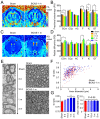
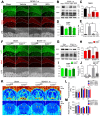
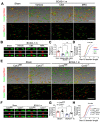
Rational: Myelin loss is a characteristic feature of both ischemic white matter disease and its associated vascular dementia, and is a hallmark of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion due to carotid artery stenosis. Yet the cellular mechanisms involved in ischemic dysmyelination are not well-understood, and no effective treatment has emerged to prevent or slow hypoperfusion-related demyelination. In a study employing the bilateral common carotid artery stenosis (BCAS) mouse model, we found reduced cerebral blood flow velocity and arteriolar pulsatility, and confirmed that prolonged BCAS provoked myelin disruption. These pathological features were associated with marked cognitive decline, in the absence of evident damage to axons. Methods: To assess the role of astroglial communication in BCAS-associated demyelination, we investigated the effect of deleting or inhibiting connexin 43 (Cx43), a constituent of astroglial gap junctions and hemichannels. Results: Genetic deletion and pharmacological inhibition of gap junctions both protected myelin integrity and rescued cognitive decline in the BCAS-treated mice. Gap junction inhibition also suppressed the transient increase in extracellular glutamate observed in the callosal white matter of wild-type mice exposed to BCAS. Conclusion: These findings suggest that astrocytic Cx43 may be a viable target for attenuating the demyelination and cognitive decline associated with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.
Keywords: astrocyte; connexin 43; ischemic white matter disease; myelin injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Characterization of White Matter Injury in a Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion.Stroke. 2016 Feb;47(2):542-7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.011679. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Stroke. 2016. PMID: 26670084
-
Fingolimod Protects Against Ischemic White Matter Damage by Modulating Microglia Toward M2 Polarization via STAT3 Pathway.Stroke. 2017 Dec;48(12):3336-3346. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.018505. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Stroke. 2017. PMID: 29114096 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytic CXCL5 hinders microglial phagocytosis of myelin debris and aggravates white matter injury in chronic cerebral ischemia.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 May 3;20(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02780-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37138312 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate receptors and white matter stroke.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Feb 16;694:86-92. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.11.031. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 30476568 Review.
-
Connexin 43/47 channels are important for astrocyte/ oligodendrocyte cross-talk in myelination and demyelination.J Biosci. 2018 Dec;43(5):1055-1068. doi: 10.1007/s12038-018-9811-0. J Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30541963 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Connexins, Pannexins and Gap Junctions in Perinatal Brain Injury.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 18;10(6):1445. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061445. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connexin43 promotes angiogenesis through activating the HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway under chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021 Oct;41(10):2656-2675. doi: 10.1177/0271678X211010354. Epub 2021 Apr 25. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2021. PMID: 33899559 Free PMC article.
-
A brief overview of a mouse model of cerebral hypoperfusion by bilateral carotid artery stenosis.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023 Nov;43(2_suppl):18-36. doi: 10.1177/0271678X231154597. Epub 2023 Mar 8. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023. PMID: 36883344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relationship Between Pre-existing Coronary Heart Disease and Cognitive Impairment Is Partly Explained by Reduced Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in the Subjects Without Clinical Heart Failure: A Cross-Sectional Study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 May 11;16:835900. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.835900. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35634203 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Alleviates Demyelination Through Regulating Microglial Phenotype Transformation to Mitigate Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in Mice with Vascular Dementia.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 May;59(5):3140-3158. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02712-3. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35267135
References
-
- Johnston SC, O'Meara ES, Manolio TA, Lefkowitz D, O'Leary DH, Goldstein S. et al. Cognitive impairment and decline are associated with carotid artery disease in patients without clinically evident cerebrovascular disease. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:237–47. - PubMed
-
- Buratti L, Balucani C, Viticchi G, Falsetti L, Altamura C, Avitabile E. et al. Cognitive deterioration in bilateral asymptomatic severe carotid stenosis. Stroke. 2014;45:2072–7. - PubMed
-
- Mathiesen EB, Waterloo K, Joakimsen O, Bakke SJ, Jacobsen EA, Bonaa KH. Reduced neuropsychological test performance in asymptomatic carotid stenosis: The Tromso Study. Neurology. 2004;62:695–701. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

