Normal-pressure hydrocephalus: A critical review
- PMID: 31285787
- PMCID: PMC6601311
- DOI: 10.1590/1980-57642018dn13-020001
Normal-pressure hydrocephalus: A critical review
Erratum in
-
Errata.Dement Neuropsychol. 2019 Jul-Sep;13(3):361. doi: 10.1590/1980-57642018dn13-030016. Dement Neuropsychol. 2019. PMID: 31555412 Free PMC article.
Abstract
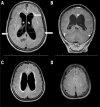
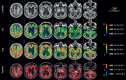
Normal-pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) is a potentially reversible syndrome characterized by enlarged cerebral ventricles (ventriculomegaly), cognitive impairment, gait apraxia and urinary incontinence. A critical review of the concept, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of both idiopathic and secondary NPH was conducted. We searched Medline and PubMed databases from January 2012 to December 2018 using the keywords "normal-pressure hydrocephalus" / "idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus" / "secondary normal-pressure hydrocephalus" / "NPH" / "ventriculoperitoneal shunt". The initial search produced 341 hits. After careful selection, a total of 54 articles were chosen and additional relevant studies were included during the process of writing this article. NPH is an important cause of potentially reversible dementia, frequent falls and recurrent urinary infections in the elderly. The clinical and imaging features of NPH may be incomplete or nonspecific, posing a diagnostic challenge for medical doctors and often requiring expert assessment to minimize unsuccessful surgical treatments. Recent advances resulting from the use of non-invasive MRI methods for quantifying cerebral blood flow, in particular arterial spin-labeling (ASL), and the frequent association of NPH and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), offer new avenues to understand and treat NPH.
A hidrocefalia de pressão normal (HPN) é uma síndrome potencialmente reversível marcada por ventrículos cerebrais alargados (ventriculomegalia), declínio cognitivo, apraxia da marcha e incontinência urinária. Revisar criticamente o conceito, a fisiopatologia, o diagnóstico e o tratamento da HPN idiopática e secundária. Os autores acessaram as bases de dados Medline e Pubmed entre janeiro de 2012 e dezembro de 2018, utilizando as palavras-chave “normal-pressure hydrocephalus” / “idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus” / “secondary normal-pressure hydrocephalus” / “NPH” / “ventriculoperitoneal shunt”. A busca inicial resultou em 341 artigos. Após cuidadosa seleção, 54 estudos foram escolhidos e pesquisas adicionais foram incluídas durante o processo de elaboração do manuscrito. A HPN é uma importante causa de demência potencialmente reversível, quedas frequentes e infecção urinária recorrente em idosos. As características clínicas e de imagem da HPN podem ser incompletas ou inespecíficas, de modo que este se torna um diagnóstico difícil para médicos. Não raro uma avaliação por especialista é necessária, visando minimizar tratamentos cirúrgicos ineficazes. Avanços recentes advindos do uso não invasivo de ressonância magnética para quantificação do fluxo sanguíneo cerebral, em particular arterial spin-labeling (ASL), assim como a usual associação entre HPN e apneia obstrutiva do sono representam novos meios de entender e de tratar a HPN.
Keywords: cerebral blood flow; falls; incontinence; normal-pressure hydrocephalus; reversible dementia; spinal tap test.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Missori P, Paolini S, Currà A. From congenital to idiopathic adult hydrocephalus A historical research. Brain. 2010;133:1836–1849. - PubMed
-
- Hakim S, Adams RD. The special clinical problem of symptomatic hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure Observations on cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics. J Neurol Sci. 1965;2:307–327. - PubMed
-
- Adams RD, Fisher CM, Hakim S, Ojemann RG, Sweet WH. Symptomatic occult hydrocephalus with "normal" cerebrospinal-fluid pressure A treatable syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1965;273:117–126. - PubMed
-
- Wallenstein MB, McKhann GM., 2nd Salomón Hakim and the discovery of normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 2010;67(1):155–159. - PubMed
-
- Shenkin HA, Greenberg J, Bouzarth WF, Gutterman P, Morales JO. Ventricular shunting for relief of senile symptoms. JAMA. 1973;225:1486–1489. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

