CT-based radiomics features analysis for predicting the risk of anterior mediastinal lesions
- PMID: 31285873
- PMCID: PMC6588768
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2019.05.32
CT-based radiomics features analysis for predicting the risk of anterior mediastinal lesions
Abstract
Background: To retrospectively validate CT-based radiomics features for predicting the risk of anterior mediastinal lesions.
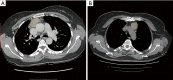
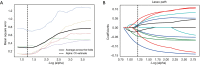
Methods: A retrospective study was performed through February 2013 to March 2018 on 298 patients who had pathologically confirmed anterior mediastinal lesions. The patients all underwent CT scans before their treatment, including 130 unenhanced computed tomography (UECT) and 168 contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) scans. The lesion areas were delineated, and a total of 1,029 radiomics features were extracted. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (Lasso) algorithm method was used to select the radiomics features significantly associated with discrimination of high-risk from low-risk lesions in the anterior mediastinum. Then, 8-fold and 3-fold cross-validation logistic regression (LR) models were taken as the feature selection classifiers to build the radiomics models for UECT and CECT scan respectively. The predictive performance of the radiomics features was evaluated based on the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve.
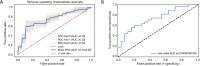
Results: Each of the two radiomics classifiers included the optimal 12 radiomic features. In terms of the area under ROC curve, using the radiomics model in discriminating high-risk lesions from the low-risks, CECT images accounted for 74.1% with a sensitivity of 66.67% and specificity of 64.81%. Meanwhile, UECT images were 84.2% with a sensitivity of 71.43% and specificity of 74.07%.
Conclusions: The association of the two proposed CT-based radiomics features with the discrimination of high and low-risk lesions in anterior mediastinum was confirmed, and the radiomics features of the UECT scan were proven to have better prediction performance than the CECT's in risk grading.
Keywords: Radiomics; anterior mediastinum; contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT); histologic grade; unenhanced computed tomography (UECT).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development and Validation of a CT-Based Radiomics Nomogram in Patients With Anterior Mediastinal Mass: Individualized Options for Preoperative Patients.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 8;12:869253. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.869253. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35875092 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiating Peripherally Located Pulmonary Noncalcified Hamartoma From Carcinoid Using CT Radiomics Approaches.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2023 May-Jun 01;47(3):402-411. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000001414. Epub 2023 Jan 17. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2023. PMID: 37185003 Clinical Trial.
-
CT-based radiomics for differentiating peripherally located pulmonary sclerosing pneumocytoma from carcinoid.Med Phys. 2024 Jun;51(6):4219-4230. doi: 10.1002/mp.17037. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38507783
-
Machine-learning-based computed tomography radiomic analysis for histologic subtype classification of thymic epithelial tumours.Eur J Radiol. 2020 May;126:108929. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108929. Epub 2020 Mar 2. Eur J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32169748
-
Radiomics vs radiologist in bladder and renal cancer. Results from a systematic review.Cent European J Urol. 2023;76(1):12-19. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2023.252. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Cent European J Urol. 2023. PMID: 37064257 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Contrast-enhanced CT-based radiomics model for differentiating risk subgroups of thymic epithelial tumors.BMC Med Imaging. 2022 Mar 6;22(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00768-8. BMC Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35249531 Free PMC article.
-
CT-based radiomics analysis for differentiation between thymoma and thymic carcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2022 May;14(5):1342-1352. doi: 10.21037/jtd-21-1948. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35693628 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of 2D and 3D radiomics features with conventional features based on contrast-enhanced CT images for preoperative prediction the risk of thymic epithelial tumors.Radiol Oncol. 2025 Feb 27;59(1):69-78. doi: 10.2478/raon-2025-0016. eCollection 2025 Mar 1. Radiol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40014788 Free PMC article.
-
Anterior Mediastinal Lesion Segmentation Based on Two-Stage 3D ResUNet With Attention Gates and Lung Segmentation.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 8;10:618357. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.618357. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33634027 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of radiomics model for preoperative risk categorization in thymic epithelial tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Imaging. 2023 Aug 29;23(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12880-023-01083-6. BMC Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37644397 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
