Association of Plasma Levels of Nitric Oxide Oxidative Metabolites with Acute Stroke in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department of a Low-Middle Income Country
- PMID: 31285918
- PMCID: PMC6594247
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9206948
Association of Plasma Levels of Nitric Oxide Oxidative Metabolites with Acute Stroke in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department of a Low-Middle Income Country
Abstract
Introduction: Acute stroke incites an inflammatory reaction in the brain's microvasculature, activating formation of nitric oxide oxidative metabolites, nitrate and nitrite (NOx, collectively), measurable in plasma. Our objectives were to investigate plasma NOx in patients with acute stroke presenting to the Emergency Department (ED) and to determine if it could (i) differentiate between ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke; (ii) predict clinical outcomes.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in the ED of Aga Khan University Hospital, from January 1 to December 31, 2016. Participants were enrolled if they had clinical acute stroke with confirmatory brain imaging to differentiate between ischemia and hemorrhage. Clinical demographic information, ancillary blood, and diagnostic specimens were collected as per standard of care since the center follows stroke algorithmic guidelines. Plasma NOx analysis was performed using high performance liquid chromatography. Clinical outcomes were assessed using Barthel Index and Modified Rankin Score. Data was analyzed using SPSS 19 and expressed in medians with interquartile ranges. Nonparametric tests were applied for comparing among groups. Pearson's correlation was used to determine associations with aforementioned stroke severity and disability scales.
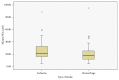
Results: Seventy-five patients were enrolled, with median age of 57 years (IQR 47-66 years), 53 (71%) were males, and 46 (61%) had ischemic stroke. Overall, median NOx was 20.8 μM (IQR 13.4-35.3); there was no statistically significant difference between NOx in ischemic versus hemorrhagic stroke (21.2 μM vs. 17.9 μM; p=0.2). However, there was a significant positive correlation between NOx levels and aforementioned acute stroke scales [r(73)=0.417, p=0.0001], for both.
Conclusion: Although plasma NOx could not differentiate between ischemia and hemorrhage, higher levels of the biomarker did show associations with poststroke disability scales. Further study with more patients in a multicenter trial is warranted to establish the real biomarker potential of plasma NOx in acute stroke.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plasma nitric oxide (nitrate/nitrite) levels in acute stroke and their relationship with severity and outcome.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2003 Mar-Apr;12(2):82-7. doi: 10.1053/jscd.2003.9. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2003. PMID: 17903909
-
Serum nitrate and nitrite levels in patients with hypertension and ischemic stroke depend on diet: a multicenter study.Clin Biochem. 2015 Jan;48(1-2):29-32. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2014.10.010. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Clin Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25445235
-
Temporal profiles of blood pressure, circulating nitric oxide, and adrenomedullin as predictors of clinical outcome in acute ischemic stroke patients.Mol Med Rep. 2016 May;13(5):3724-34. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5001. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27035412 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oxidative stress in post-acute ischemic stroke patients after intensive neurorehabilitation.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2012 Nov;9(4):266-73. doi: 10.2174/156720212803530717. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22873723
-
CSF nitric oxide metabolites are associated with activity and progression of multiple sclerosis.Neurology. 2004 Oct 26;63(8):1439-45. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000142043.32578.5d. Neurology. 2004. PMID: 15505162
Cited by
-
Adrenomedullin Is a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021 Jun 11;43(1):324-334. doi: 10.3390/cimb43010027. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34208106 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

