Trends in surgical and ablative treatment of localised renal cell carcinoma: A review of publication trends over 16 years (2000-2015)
- PMID: 31285923
- PMCID: PMC6600061
- DOI: 10.1080/2090598X.2019.1590516
Trends in surgical and ablative treatment of localised renal cell carcinoma: A review of publication trends over 16 years (2000-2015)
Abstract
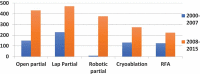
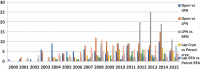
Objective: To investigate the bibliometric (publication) trends in surgical and ablative treatment of localised renal cell carcinoma (RCC) over a period of 16-years, from 2000 to 2015, as publication trends reflect clinical practice and new innovations. Material and methods: We performed a systematic review using PubMed over a 16-year period from 2000 to 2015 for all published papers on surgical and ablative management of renal tumours. Data were further analysed in two time periods, period-1 (2000-2007) and period-2 (2008-2015). Results: During the last 16 years a total of 2415 papers were published on surgical (n = 1662, 69%) and ablative (n = 753, 31%) management of RCC. This included partial nephrectomy (PN; n = 1662, 69%), cryoablation (CA; n = 405, 17%), and radiofrequency ablation (RFA; n = 348, 14%). When comparing the two time periods for PN, during period-2, the change was +189% (P < 0.001), +69% (P = 0.004) and +4600% (P < 0.001) for open PN, laparoscopic PN and robotic PN, respectively. Regarding ablative techniques, a change of +109% (P = 0.002) and +78% (P = 0.036) was seen for CA and RFA, respectively. There was also a significant rise in percutaneous CA when compared to laparoscopic CA (P < 0.002). Conclusions: There has been a rise in all forms of PN and ablative techniques over the last 16 years. This rise has been particularly steep for robotic PN potentially reflecting a change in surgical practice. Abbreviations: CA: cryoablation; CC: correlation coefficient; MIS: minimally invasive surgery/surgical; NSS: nephron-sparing surgery; (L)(O)(R)PN: (laparoscopic) (open) (robotic) partial nephrectomy; PRISMA: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses; RFA: radiofrequency ablation; RN: radical nephrectomy; SRM: small renal mass.
Keywords: Publication trends; cryoablation; partial nephrectomy; radiofrequency ablation; renal cancer; robotic.
Figures
References
-
- Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Bensalah K et al. EAU guidelines on renal cancer, 2016 update. cited 2018 December Available from: http://uroweb.org/guideline/renal-cell-carcinoma/.
-
- Volpe A, Panzarella T, Rendon R, et al. The natural history of incidentally detected small renal masses. Cancer. 2004;100:738–745. - PubMed
-
- Rai BP, Ali A, Raslan M, et al. Fate of indeterminate lesions detected on noncontrast computed tomography scan for suspected urolithiasis: a retrospective cohort study with a minimum follow-up of 15 months. Urology. 2014;84:1272–1274. - PubMed
-
- Gu L, Ma X, Li H, et al. Comparison of oncologic outcomes between partial and radical nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Oncol. 2016;25:385–393. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources