Management of Fish Bone-Induced Liver Abscess with Foreign Body Left In Situ
- PMID: 31285930
- PMCID: PMC6594292
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9075198
Management of Fish Bone-Induced Liver Abscess with Foreign Body Left In Situ
Abstract
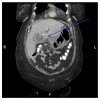
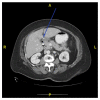
Pyogenic liver abscess, having experienced an evolving pathogenesis over the years, still remains a serious problem with significant morbidity. Iatrogenic and ascending biliary infections are the most common known etiologies for hepatic abscess. Here we report an interesting case of an elderly lady admitted with abdominal pain due to a pyogenic liver abscess in the left liver lobe which was attributed to perforation by an ingested fish bone. The authors also reviewed literature for management for this rare case as there are no standard guidelines. Our patient was successfully treated with antibiotics and percutaneous drainage with foreign body left in situ.
Figures


References
-
- Kaplan G. G., Gregson D. B., Laupland K. B. Population-based study of the epidemiology of and the risk factors for pyogenic liver abscess. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology: The Official Clinical Practice Journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. 2004;2(11):1032–1038. doi: 10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00459-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- A. L. Abscess of the liver of unusual origin. NY Med J. 1898:177-8.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

