Randomized phase II study of pemetrexed-cisplatin or docetaxel-cisplatin plus thoracic intensity-modulated radiation therapy in patients with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 31285955
- PMCID: PMC6610059
Randomized phase II study of pemetrexed-cisplatin or docetaxel-cisplatin plus thoracic intensity-modulated radiation therapy in patients with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
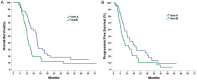
Systemic chemotherapy is the standard treatment modality for stage IV lung adenocarcinoma patients with EGFR wild-type or unknown mutation status. Recent years, there is increasing evidence showed that selected patients with stage IV disease could benefit from aggressive thoracic radiotherapy. Either pemetrexed or docetaxel, combined with cisplatin, can be used for patients with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma. However, no prospective trials have confirmed that Pem-Cis was superior to Doc-Cis in lung adenocarcinoma. In this randomized phase 2 trial, we evaluated survival outcomes, and toxicity of Pemetrexed-Cisplatin (arm A) or Docetaxel-Cisplatin (arm B) with concurrent IMRT to the primary tumor for stage IV lung adenocarcinoma patients with EGFR wild-type or unknown mutation status. Totally, 101 patients were randomly assigned (50 in arm A and 51 in arm B). Using an intention-to-treat analysis, one-year survival rates were 72.0% and 52.9%, respectively (P=0.020). Progression-free survival was also significantly improved in the arm A (median, 12.6 v 7.5 months, P=0.013). The incidence and severity of acute pneumonitis and esophagitis was similar between two arms. Although more of grade 3 or 4 anemia and thrombocytopenia in arm A, and higher rates grade 3 or 4 neutropenia, and leukopenia were observed in arm B. Pem-Cis first-line chemotherapy with concurrent radiation therapy for stage IV lung adenocarcinoma patients with EGFR wild-type or unknown mutation status represents a potential treatment option with acceptable toxicity and high overall survival rates.
Keywords: Stage IV; concurrent chemoradiotherapy; docetaxel; lung adenocarcinoma; pemetrexed; phase II study.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Randomized Phase III Study of Docetaxel Plus Cisplatin Versus Pemetrexed Plus Cisplatin as First-line Treatment of Nonsquamous Non-Small-cell Lung Cancer: A TRAIL Trial.Clin Lung Cancer. 2017 Jul;18(4):e289-e296. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Clin Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28185792 Clinical Trial.
-
Final results from a Phase II study of pemetrexed and cisplatin with concurrent thoracic radiation after Pem-Cis induction in patients with unresectable locally advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2015 May;88(2):160-6. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.02.014. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25758556 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized phase II study of chemoradiotherapy with cisplatin + S-1 versus cisplatin + pemetrexed for locally advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: SPECTRA study.Lung Cancer. 2020 Mar;141:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.01.008. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31955002 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized phase II study comparing weekly docetaxel-cisplatin vs. gemcitabine-cisplatin in elderly or poor performance status patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017 May;79(5):873-880. doi: 10.1007/s00280-017-3289-6. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28341958 Clinical Trial.
-
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: preclinical and early clinical data.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004 Feb;18(1):41-53. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8588(03)00138-2. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004. PMID: 15005280 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-25-3p promotes cisplatin resistance in Non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) through adjusting PTEN/PI3K/AKT route.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3219-3228. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1939577. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34266345 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma by integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 8;10:1323344. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1323344. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38259856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD44 inhibition attenuates EGFR signaling and enhances cisplatin sensitivity in human EGFR wild‑type non‑small‑cell lung cancer cells.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Jun;45(6):1783-1792. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4562. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32236608 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of primary tumor volume on survival of concurrent chemoradiotherapy in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Med. 2024 Sep;13(17):e70221. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70221. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39279741 Free PMC article.
-
Symptomatic Radiation Pneumonitis in NSCLC Patients Receiving EGFR-TKIs and Concurrent Once-daily Thoracic Radiotherapy: Predicting the Value of Clinical and Dose-volume Histogram Parameters.Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022 Jun 20;25(6):409-419. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2022.102.17. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35747920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Scagliotti GV, De Marinis F, Rinaldi M, Crino L, Gridelli C, Ricci S, Matano E, Boni C, Marangolo M, Failla G, Altavilla G, Adamo V, Ceribelli A, Clerici M, Di Costanzo F, Frontini L, Tonato M. Phase III randomized trial comparing three platinum-based doublets in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002;20:4285–4291. - PubMed
-
- Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, Zhu J, Johnson DH. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:92–98. - PubMed
-
- Morgensztern D, Waqar S, Subramanian J, Gao F, Govindan R. Improving survival for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results survey from 1990 to 2005. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4:1524–1529. - PubMed
-
- Sakurai H, Asamura H, Goya T, Eguchi K, Nakanishi Y, Sawabata N, Okumura M, Miyaoka E, Fujii Y. Survival differences by gender for resected non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective analysis of 12,509 cases in a Japanese lung cancer registry study. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:1594–1601. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous