Inhibition of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by combination of Afatinib with PD0325901, a MEK inhibitor
- PMID: 31285959
- PMCID: PMC6610054
Inhibition of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by combination of Afatinib with PD0325901, a MEK inhibitor
Abstract
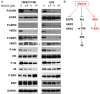
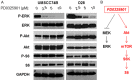
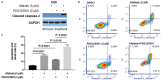
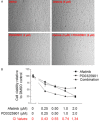
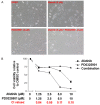
ErbB family members that contain EGFR, HER2, HER3 and HER4 play important roles in many cancer types, including head and neck; however, inhibition of these receptors by small molecule kinase inhibitors showed limited results due to compensatory up-regulation of some key survival signaling pathways. Here, we explore the effectiveness of Afatinib, an irreversible inhibitor of EGFR, HER2, and HER4, in combination with the MEK inhibitor PD0325901 to inhibit cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). We treated two cisplatin-resistant HNSCC cell lines, UMSCC74B and O28, with Afatinib, PD0325901, or a combination, and measured signaling pathways, cell proliferation, and survival. We found that Afatinib blocked Akt/mTOR activity and phosphorylation of EGFR, HER2 and HER3, but up-regulated MEK/ERK signaling. Interestingly, MEK inhibitor PD0325901 blocked ERK phosphorylation, but elevated phosphorylation of Akt and mTOR pathways. Similarly, Afatinib and PD0325901 inhibited all these pathways and synergistically suppressed cell proliferation and survival. Our data demonstrate that Afatinib in combination with MEK inhibitors could provide a potential novel therapy for cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell cancer.
Keywords: Afatinib; Akt; EGFR; EGFR inhibitors; ERK; HNSCC; Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; MEK; MEK inhibitor; PD0325901; PI3K; cisplatin-resistant HNSCC; mTOR.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by the SRC/ETS-1 signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2019 May 22;19(1):485. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5664-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31118072 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneously targeting ErbB family kinases and PI3K in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Oncol. 2022 Aug;131:105939. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2022.105939. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Oral Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35667295
-
Simultaneous targeting of EGFR, HER2, and HER4 by afatinib overcomes intrinsic and acquired cetuximab resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines.Mol Oncol. 2018 Jun;12(6):830-854. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12197. Epub 2018 May 1. Mol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29603584 Free PMC article.
-
The challenge of blocking a wider family members of EGFR against head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Oral Oncol. 2015 May;51(5):423-30. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.02.092. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Oral Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25753560 Review.
-
Targeting EGFR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling enhances radiosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015 Jun;19(6):795-805. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2015.1012157. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015. PMID: 25652792 Review.
Cited by
-
Combination Treatment With Inhibitors of ERK and Autophagy Enhances Antitumor Activity of Betulinic Acid in Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer In Vivo and In Vitro.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 29;12:684243. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.684243. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34267658 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin and trametinib: a rational combination for treatment of NSCLC.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Jul 25;17(12):3211-3223. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.62752. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34421360 Free PMC article.
-
Translational Insights and New Therapeutic Perspectives in Head and Neck Tumors.Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 19;9(8):1045. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9081045. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34440249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of resistance in head and neck cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Sep 1;10(9):2742-2751. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33042614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concurrent inhibition of ErbB family and MEK/ERK kinases to suppress non-small cell lung cancer proliferation.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Mar 15;12(3):847-856. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32269717 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
