An information network flow approach for measuring functional connectivity and predicting behavior
- PMID: 31286688
- PMCID: PMC6710195
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1346
An information network flow approach for measuring functional connectivity and predicting behavior
Abstract
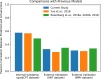
Introduction: Connectome-based predictive modeling (CPM) is a recently developed machine-learning-based framework to predict individual differences in behavior from functional brain connectivity (FC). In these models, FC was operationalized as Pearson's correlation between brain regions' fMRI time courses. However, Pearson's correlation is limited since it only captures linear relationships. We developed a more generalized metric of FC based on information flow. This measure represents FC by abstracting the brain as a flow network of nodes that send bits of information to each other, where bits are quantified through an information theory statistic called transfer entropy.
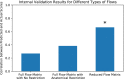
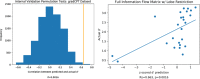
Methods: With a sample of individuals performing a sustained attention task and resting during functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) (n = 25), we use the CPM framework to build machine-learning models that predict attention from FC patterns measured with information flow. Models trained on n - 1 participants' task-based patterns were applied to an unseen individual's resting-state pattern to predict task performance. For further validation, we applied our model to two independent datasets that included resting-state fMRI data and a measure of attention (Attention Network Task performance [n = 41] and stop-signal task performance [n = 72]).
Results: Our model significantly predicted individual differences in attention task performance across three different datasets.
Conclusions: Information flow may be a useful complement to Pearson's correlation as a measure of FC because of its advantages for nonlinear analysis and network structure characterization.
Keywords: functional connectivity; information flow; predictive model; resting-state fMRI connectivity; sustained attention.
© 2019 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures






References
-
- Ahuja, R. K. , Magnanti, T. L. , & Orlin, J. B. (2014). Network flows theory, algorithms and applications. Harlow, London, UK: Paerson Education.
-
- Deligianni, F. , Robinson, E. , Beckmann, C. F. , Sharp, D. , Edwards, A. D. , & Rueckert, D. (2011). Inference of functional connectivity from direct and indirect structural brain connections. In 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro (pp. 849–852). IEEE.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

