Acute stress-induced change in polysialic acid levels mediated by sialidase in mouse brain
- PMID: 31289315
- PMCID: PMC6616613
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46240-6
Acute stress-induced change in polysialic acid levels mediated by sialidase in mouse brain
Abstract
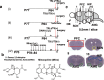
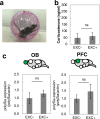
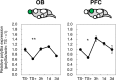
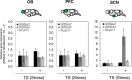
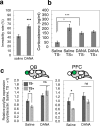
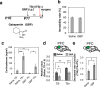
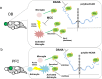
Stress is an important environmental factor influencing human behaviour and causing several mental disorders. Alterations in the structure of polysialic acid (polySia/PSA) due to genetic alterations in ST8SIA2, which encodes a polySia-synthesizing enzyme, are related to certain mental disorders. However, whether stress as an environmental factor leads to changes in polySia structure is unknown. Here we studied the effects of acute stress on polySia expression and found reductions in both the quantity and quality of polySia in the olfactory bulb and prefrontal cortex, even with short-term exposure to acute stress. The use of inhibitors for sialidase, microglia and astrocytes revealed that these declines were due to a transient action of sialidase from microglia and astrocytes in the olfactory bulb and prefrontal cortex, respectively. These data suggest that sialidase dynamically regulates polySia expression in a brain region-specific manner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

