Role of caprin-1 in carcinogenesis
- PMID: 31289466
- PMCID: PMC6540157
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10295
Role of caprin-1 in carcinogenesis
Abstract
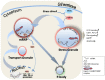
RNA-binding proteins serve an essential role in post-transcriptional gene regulation. Cytoplasmic activation/proliferation-associated protein-1 (caprin-1) is an RNA-binding protein that participates in the regulation of cell cycle control-associated genes. Caprin-1 acts alone or in combination with other RNA-binding proteins, such as RasGAP SH3-domain-binding protein 1 and fragile X mental retardation protein. In the tumorigenesis process, caprin-1 primarily functions by activating cell proliferation and upregulating the expression of immune checkpoint proteins. Through the formation of stress granules, caprin-1 is also involved in the process by which tumor cells adapt to adverse conditions, which contributes to radiation and chemotherapy resistance. Given its role in various clinical malignancies, caprin-1 holds the potential to be used as a biomarker and a target for the development of novel therapeutics. The present review describes this newly identified putative oncogenic protein and its possible impact on tumorigenesis.
Keywords: RNA-binding proteins; cytoplasmic activation/proliferation-associated protein-1; epigenetics; tumorigenesis.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
