Ampelopsin-sodium induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines by promoting tubulin polymerization in vitro
- PMID: 31289488
- PMCID: PMC6540484
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10288
Ampelopsin-sodium induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines by promoting tubulin polymerization in vitro
Abstract
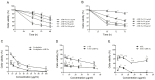
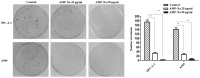
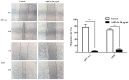
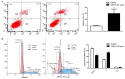
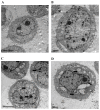
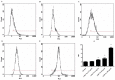
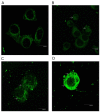
Previous studies have demonstrated that ampelopsin (AMP), a type of flavonoid isolated from the stems and leaves of Ampelopsis grossedentata, exhibits anti-cancer activity in various types of cancer. Conversion of AMP into its sodium salt (AMP-Na) conferred enhanced solubility and stability to it. The present study aimed to evaluate the anti-cancer activity of AMP-Na in human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines and to investigate its mechanisms of action. Cell proliferation and viability were assessed by MTT and colony formation assays, and cell migration was determined using a scratch wound healing assay. The cell cycle distribution, apoptosis rate and tubulin immunofluorescence intensity were analyzed using flow cytometry, the cell ultra-microstructure was examined using transmission electron microscopy and the accumulation of tubulin was determined using laser confocal microscopy. The results demonstrated that AMP-Na significantly inhibited the proliferation, clonogenicity and migration of human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Furthermore, AMP-Na induced SPC-A-1 cell apoptosis, and promoted tubulin polymerization. The results suggested that the underlying mechanisms of AMP-Na may involve targeting of microtubules and tubulin polymerization to subsequently disrupt mitosis and induce cell cycle arrest at the S-phase.
Keywords: ampelopsin sodium; anti-tumor; apoptosis; human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines; tubulin polymerization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ampelopsin targets in cellular processes of cancer: Recent trends and advances.Toxicol Rep. 2022 Jul 27;9:1614-1623. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.07.013. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36561961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ampelopsin sodium induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma SPC-A-1 cell line.Pharmazie. 2016 Aug 1;71(8):455-459. doi: 10.1691/ph.2016.6571. Pharmazie. 2016. PMID: 29442032
-
Synergistic cytotoxicity of ampelopsin sodium and carboplatin in human non-small cell lung cancer cell line SPC-A1 by G1 cell cycle arrested.Chin J Integr Med. 2017 Feb;23(2):125-131. doi: 10.1007/s11655-016-2591-1. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Chin J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 27299463
-
Molecular mechanisms of ampelopsin from Ampelopsis megalophylla induces apoptosis in HeLa cells.Oncol Lett. 2017 Sep;14(3):2691-2698. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6520. Epub 2017 Jul 4. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28928812 Free PMC article.
-
Ampelopsin inhibits human glioma through inducing apoptosis and autophagy dependent on ROS generation and JNK pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Aug;116:108524. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.136. Epub 2019 May 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31108349
Cited by
-
A network pharmacology approach to evaluate the synergistic effect of dihydromyricetin and myricitrin in vine tea on the proliferation of B16F10 cells.Front Nutr. 2022 Sep 8;9:993133. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.993133. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36185647 Free PMC article.
-
Ampelopsin targets in cellular processes of cancer: Recent trends and advances.Toxicol Rep. 2022 Jul 27;9:1614-1623. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.07.013. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36561961 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nazir HF, AlFutaisi A, Zacharia M, Elshinawy M, Mevada ST, Alrawas A, Khater D, Jaju D, Wali Y. Vincristine-induced neuropathy in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Oman: Frequent autonomic and more severe cranial nerve involvement. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2017;64 doi: 10.1002/pbc.26677. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen XM, Xie XB, Zhao Q, Wang F, Bai Y, Yin JQ, Jiang H, Xie XL, Jia Q, Huang G. Ampelopsin induces apoptosis by regulating multiple c-Myc/S-phase kinase-associated protein 2/F-box and WD repeat-containing protein 7/histone deacetylase 2 pathways in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11:105–112. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2733. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
