Inhibition of proliferation and migration of melanoma cells by ketoconazole and Ganoderma immunomodulatory proteins
- PMID: 31289567
- PMCID: PMC6539804
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10355
Inhibition of proliferation and migration of melanoma cells by ketoconazole and Ganoderma immunomodulatory proteins
Abstract
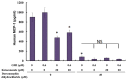
Ketoconazole, an antifungal agent, has been used to inhibit hormone synthesis in types of prostate and breast cancer. Immunomodulatory proteins of Ganoderma microsporum (GMI) inhibit the tumor necrosis factor-α- and epidermal growth factor-induced metastatic ability of lung cancer cells. Cutaneous malignant melanoma is a highly invasive and metastatic skin cancer. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is limited understanding regarding the effects of ketoconazole and GMI on melanoma. The current study aimed to investigate the inhibitory effects of GMI combined with ketoconazole on melanoma survival and metastasis. The effects of GMI combined with ketoconazole on the viability, migration and protein expression of melanoma cells were determined by MTT assay, Boyden chamber assay and western blot analysis, respectively. The expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) was investigated by enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay. The present results indicate that ketoconazole enhances the GMI-induced decrease in proliferation and migration of A375.S2 melanoma cells in a concentration-dependent manner. Ketoconazole was identified to reduce the level of GMI-induced phosphorylated-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (p-AMPK)-α and autophagy; however, ketoconazole did not affect p-AMPK-β levels in A375.S2 cells. In addition, ketoconazole and dorsomorphin dihydrochloride, an AMPK inhibitor, were revealed to reduce MCP-1 secretion in A375.S2 cells. In summary, the present study revealed that ketoconazole enhances GMI-inhibited proliferation and migration of A375.S2 melanoma cancer cells, and inhibits the secretion of MCP-1.
Keywords: Ganoderma microsporum; adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; ketoconazole; melanoma; monocyte chemoattractant protein-1.
Figures




References
-
- Agarwal SK, Salem AH, Danilov AV, Hu B, Puvvada S, Gutierrez M, Chien D, Lewis LD, Wong SL. Effect of ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A inhibitor, on the pharmacokinetics of venetoclax, a BCL-2 inhibitor, in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017;83:846–854. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13175. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Figg WD, Woo S, Zhu W, Chen X, Ajiboye AS, Steinberg SM, Price DK, Wright JJ, Parnes HL, Arlen PM, et al. A phase I clinical study of high dose ketoconazole plus weekly docetaxel for metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer. J Urol. 2010;183:2219–2226. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2010.02.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lin CH, Hsiao YM, Ou CC, Lin YW, Chiu YL, Lue KH, Chang JG, Ko JL. GMI, a Ganoderma immunomodulatory protein, down-regulates tumor necrosis factor α-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 via NF-κB pathway in human alveolar epithelial A549 cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2010;58:12014–12021. doi: 10.1021/jf103068w. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
