MICROmanagement of Runx2 Function in Skeletal Cells
- PMID: 31289715
- PMCID: PMC6615570
- DOI: 10.1007/s40610-019-0115-4
MICROmanagement of Runx2 Function in Skeletal Cells
Abstract
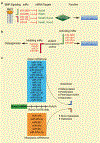
Purpose of review-: Precise and temporal expression of Runx2 and its regulatory transcriptional network is a key determinant for the intricate cellular and developmental processes in adult bone tissue formation. This review analyzes how microRNA functions to regulate this network, and how dysregulation results in bone disorders.
Recent findings-: Similar to other biologic processes, microRNA (miRNA/miR) regulation is undeniably indispensable to bone synthesis and maintenance. There exists a miRNA-RUNX2 network where RUNX2 regulates the transcription of miRs, or is post transcriptionally regulated by a class of miRs, forming a variety of miR-RUNX2 regulatory pathways which regulate osteogenesis.
Summary-: The current review provides insights to understand transcriptional-post transcriptional regulatory network governed by Runx2 and osteogenic miRs, and is based largely from in vitro and in vivo studies. When taken together, this article discusses a new regulatory layer of bone tissue specific gene expression by RUNX2 influenced via miRNA.
Keywords: MicroRNA; Noncoding RNA; Osteoblast Differentiation; Osteoblastogenesis; Posttranscriptional Repression; Runx2.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Benjamin J. Wildman, Tanner C. Godfrey, Mohammad Rehan, Yuechuan Chen, Lubana H. Afreen and Quamarul Hassan each declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
