Down-regulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 is involved in intervertebral disc degeneration via the ERK signalling pathway
- PMID: 31290273
- PMCID: PMC6714225
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14525
Down-regulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 is involved in intervertebral disc degeneration via the ERK signalling pathway
Erratum in
-
Correction to Downregulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 is involved in intervertebral disc degeneration via the ERK signalling pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Nov;27(21):3418. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17876. Epub 2023 Aug 23. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37610082 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
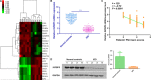
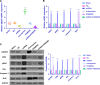
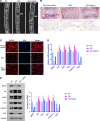
It is obvious that epigenetic processes influence the evolution of intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). However, its molecular mechanisms are poorly understood. Therefore, we tested the hypothesis that IGFBP5, a potential regulator of IDD, modulates IDD via the ERK signalling pathway. We showed that IGFBP5 mRNA was significantly down-regulated in degenerative nucleus pulposus (NP) tissues. IGFBP5 was shown to significantly promote NP cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in vitro, which was confirmed by MTT, flow cytometry and colony formation assays. Furthermore, IGFBP5 was shown to exert its effects by inhibiting the ERK signalling pathway. The effects induced by IGFBP5 overexpression on NP cells were similar to those induced by treatment with an ERK pathway inhibitor (PD98059). Moreover, qRT-PCR and Western blot analyses were performed to examine the levels of apoptosis-related factors, including Bax, caspase-3 and Bcl2. The silencing of IGFBP5 up-regulated the levels of Bax and caspase-3 and down-regulated the level of Bcl2, thereby contributing to the development of human IDD. Furthermore, these results were confirmed in vivo using an IDD rat model, which showed that the induction of Igfbp5 mRNA expression abrogated the effects of IGFBP5 silencing on intervertebral discs. Overall, our findings elucidate the role of IGFBP5 in the pathogenesis of IDD and provide a potential novel therapeutic target for IDD.
Keywords: ERK; IGFBP5; intervertebral disc degeneration; nucleus pulposus.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
miR-24-3p induces human intervertebral disc degeneration by targeting insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 and the ERK signaling pathway.Life Sci. 2020 Feb 15;243:117288. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117288. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31926246
-
Overexpressed IGFBP5 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of nucleus pulposus derived from rats with disc degeneration through inactivating the ERK/MAPK axis.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Nov;120(11):18782-18792. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29191. Epub 2019 Jul 16. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31310371
-
lncRNA HOTAIR upregulates autophagy to promote apoptosis and senescence of nucleus pulposus cells.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Mar;235(3):2195-2208. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29129. Epub 2019 Sep 3. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31478571
-
Circular RNAs in nucleus pulposus cell function and intervertebral disc degeneration.Cell Prolif. 2019 Nov;52(6):e12704. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12704. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 31621141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs in nucleus pulposus cell function and intervertebral disc degeneration.Cell Prolif. 2018 Oct;51(5):e12483. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12483. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Cell Prolif. 2018. PMID: 30039593 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tris(2-chloroethyl) Phosphate (TCEP) Elicits Hepatotoxicity by Activating Human Cancer Pathway Genes in HepG2 Cells.Toxics. 2020 Nov 20;8(4):109. doi: 10.3390/toxics8040109. Toxics. 2020. PMID: 33233533 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of IGFBP5 expression alleviates neurogenic erectile dysfunction by inducing neurovascular regeneration.Investig Clin Urol. 2025 Jan;66(1):74-86. doi: 10.4111/icu.20240325. Investig Clin Urol. 2025. PMID: 39791587 Free PMC article.
-
Cyto-Genotoxic and Transcriptomic Alterations in Human Liver Cells by Tris (2-Ethylhexyl) Phosphate (TEHP): A Putative Hepatocarcinogen.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 3;23(7):3998. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073998. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409358 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Mechanisms of Stem Cell Therapy for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Biomedicines. 2023 Sep 6;11(9):2467. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092467. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37760908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulation of IGFBP5 contributes to replicative senescence via ERK2 activation in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Apr 4;14(7):2966-2988. doi: 10.18632/aging.203999. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35378512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Postacchini F. Results of surgery compared with conservative management for lumbar disc herniations. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21:1383‐1387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

