Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome with interstitial lung disease: A holistically worked up couplet
- PMID: 31290422
- PMCID: PMC6625230
- DOI: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_258_18
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome with interstitial lung disease: A holistically worked up couplet
Abstract
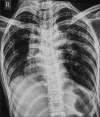
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) is an extremely subtile autosomal recessive disorder characterized by tyrosinase-positive oculocutaneous albinism (Ty-pos OCA), bleeding tendencies, and systemic complications associated to lysosomal dysfunction. The most grave complication of disease is interstitial lung disease (ILD) leading to irrevocable pulmonary fibrosis. Patients with HPS-1, HPS-2, and HPS-4 variants have a penchant to develop pulmonary fibrosis. The pulmonary involvement is characterised by progressive dyspnea hypoxemia respiratory failure and corpulmonale. The disease has an unfortunate prognosis with a high mortality rate and a poor quality of life. The options currently available in the therapeutic armamentarium are dismal with a dire need for opportune research. We hereby narrate an intriguing case scenario of a pair of siblings affected with this rare disorder with its associated ILD.
Keywords: Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome; lysosomal dysfunction; occulo-cutaneous albinism; pulmonary fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


References
-
- Hermansky F, Pudlak P. Albinism associated with hemorrhagic diathesis and unusual pigmented reticular cells in the bone marrow: Report of two cases with histochemical studies. Blood. 1959;14:162–9. - PubMed
-
- Li W, Rusiniak ME, Chintala S, Gautam R, Novak EK, Swank RT, et al. Murine Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome genes: Regulators of lysosome-related organelles. Bioessays. 2004;26:616–28. - PubMed
-
- Chiang PW, Oiso N, Gautam R, Suzuki T, Swank RT, Spritz RA. The Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 1 (HPS1) and HPS4 proteins are components of two complexes, BLOC-3 and BLOC-4, involved in the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:20332–7. - PubMed
-
- Witkop CJ, Almadovar C, Piñeiro B, Nuñez Babcock M. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS). An epidemiologic study. Ophthalmic Paediatr Genet. 1990;11:245–50. - PubMed
-
- Witkop CJ, Nuñez Babcock M, Rao GH, Gaudier F, Summers CG, Shanahan F, et al. Albinism and Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome in Puerto Rico. Bol Asoc Med P R. 1990;82:333–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

