Low-dose sirolimus in retroperitoneal lymphangioleiomyomas
- PMID: 31290423
- PMCID: PMC6625232
- DOI: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_433_18
Low-dose sirolimus in retroperitoneal lymphangioleiomyomas
Abstract
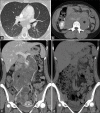
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a rare disease associated with cystic lung destruction and abdominal tumors, including lymphangioleiomyomas, which frequently occur in the retroperitoneal region. Sirolimus therapy is currently recommended for LAM patients with abnormal or declining lung function with an adjusted dose to maintain a serum trough level of 5-15 ng/mL. We describe a significant reduction of retroperitoneal lymphangioleiomyomas after treatment with low-dose sirolimus therapy (serum trough level <5 ng/mL) in a patient with sporadic LAM.
Keywords: Low-dose sirolimus; lymphangioleimyomas; lymphangioleiomyomatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Ando K, Kurihara M, Kataoka H, Ueyama M, Togo S, Sato T, et al. Efficacy and safety of low-dose sirolimus for treatment of lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Respir Investig. 2013;51:175–83. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

