The mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel is required for bone formation
- PMID: 31290742
- PMCID: PMC6685704
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.47454
The mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel is required for bone formation
Abstract
Mechanical load of the skeleton system is essential for the development, growth, and maintenance of bone. However, the molecular mechanism by which mechanical stimuli are converted into osteogenesis and bone formation remains unclear. Here we report that Piezo1, a bona fide mechanotransducer that is critical for various biological processes, plays a critical role in bone formation. Knockout of Piezo1 in osteoblast lineage cells disrupts the osteogenesis of osteoblasts and severely impairs bone structure and strength. Bone loss that is induced by mechanical unloading is blunted in knockout mice. Intriguingly, simulated microgravity treatment reduced the function of osteoblasts by suppressing the expression of Piezo1. Furthermore, osteoporosis patients show reduced expression of Piezo1, which is closely correlated with osteoblast dysfunction. These data collectively suggest that Piezo1 functions as a key mechanotransducer for conferring mechanosensitivity to osteoblasts and determining mechanical-load-dependent bone formation, and represents a novel therapeutic target for treating osteoporosis or mechanical unloading-induced severe bone loss.
Keywords: Piezo1; bone formation; cell biology; human; mechanosensitive ion channel; mechanotransduction; mouse; osteoblast; unloading.
© 2019, Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
WS, SC, YL, SL, YT, YX, FJ, JL, CL, GZ, DC, XJ, DZ, XG, ZL, BX, YL No competing interests declared
Figures



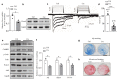
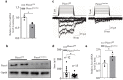

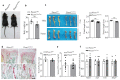

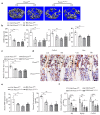


Comment in
-
Sensing the load.Elife. 2019 Oct 7;8:e50210. doi: 10.7554/eLife.50210. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31588900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen X, Wanggou S, Bodalia A, Zhu M, Dong W, Fan JJ, Yin WC, Min HK, Hu M, Draghici D, Dou W, Li F, Coutinho FJ, Whetstone H, Kushida MM, Dirks PB, Song Y, Hui CC, Sun Y, Wang LY, Li X, Huang X. A feedforward mechanism mediated by mechanosensitive ion channel PIEZO1 and tissue mechanics promotes glioma aggression. Neuron. 2018;100:799–815. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.09.046. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 31630038/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 91740114/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81830061/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 31700741/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 31825014/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 31630090/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2016YFA0500402/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China/International
- 2015CB910102/Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China/International
- 31800994/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81822026/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- AWS16J018/1226 Project/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

