Quantitative evaluation of computed and voxelwise computed diffusion-weighted imaging in breast cancer
- PMID: 31291125
- PMCID: PMC6724633
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20180978
Quantitative evaluation of computed and voxelwise computed diffusion-weighted imaging in breast cancer
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the value of computed diffusion-weighted imaging (cDWI) and voxelwise computed diffusion-weighted imaging (vcDWI) in breast cancer.
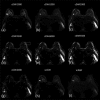
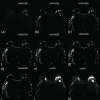
Methods: This retrospective study involved 130 patients (age range, 25-70 years; mean age ± standard deviation, 48.6 ± 10.5 years) with 130 malignant lesions, who underwent MRI examinations, including a DWI sequence, prior to needle biopsy or surgery. cDWIs with higher b-values of 1500, 2000, 2500, 3000, 3500, and 4000 s/mm2, and vcDWI were generated from measured (m) DWI with two lower b-values of 0/600, 0/800, or 0/1000 s/mm2. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast ratio (CR) of all image sets were computed and compared among different DWIs by two experienced radiologists independently. To better compare the CR with the SNR, the CR value was multiplied by 100 (CR100).
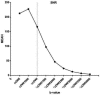
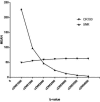
Results: The CR of vcDWI, and cDWIs, except for cDWI1000, differed significantly from that of measured diffusion-weighted imaging (mDWI) (cDWI1000: CR = 0.4904, p = 0.394; cDWI1500: CR = 0.5503, p = 0.006; cDWI2000: CR = 0.5889, p < 0.001; cDWI2500: CR = 0.6109, p < 0.001; cDWI3000: mean = 0.6214, p < 0.001; cDWI3500: CR = 0.6245, p < 0.001; cDWI4000: CR = 0.6228, p < 0.001). The vcDWI provided the highest CR, while the CRs of all cDWI image sets improved with increased b-values. The SNR of neither cDWI1000 nor vcDWI differed significantly from that of mDWI, but the mean SNRs of the remaining cDWIs were significantly lower than that of mDWI. The SNRs of cDWIs declined with increasing b-values, and the initial decrease at low b-values was steeper than the gradual attenuation at higher b-values; the CR100 rose gradually, and the two converged on the b-value interval of 1500-2000 s/mm2 .
Conclusions: The highest CR was achieved with vcDWI; this could be a promising approach easier detection of breast cancer.
Advances in knowledge: This study comprehensively compared and evaluated the value of the emerging post-processing DWI techniques (including a set of cDWIs and vcDWI) in breast cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Feasibility and Diagnostic Performance of Voxelwise Computed Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Breast Cancer.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Jun;49(6):1610-1616. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26533. Epub 2018 Oct 16. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30328211 Free PMC article.
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient-dependent voxelwise computed diffusion-weighted imaging: An approach for improving SNR and reducing T2 shine-through effects.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Apr;43(4):824-32. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25044. Epub 2015 Sep 8. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26348708
-
How to Improve the Conspicuity of Breast Tumors on Computed High b-value Diffusion-weighted Imaging.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2019 Apr 10;18(2):119-125. doi: 10.2463/mrms.mp.2018-0011. Epub 2018 Jul 13. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30012905 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical feasibility of a deep learning approach for conventional and synthetic diffusion-weighted imaging in breast cancer: Qualitative and quantitative analyses.Eur J Radiol. 2025 Jan;182:111855. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111855. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Eur J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39616946
-
Diffusion-weighted breast MRI: Clinical applications and emerging techniques.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017 Feb;45(2):337-355. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25479. Epub 2016 Sep 30. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017. PMID: 27690173 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic value of diffusion-weighted imaging with synthetic b-values in breast tumors: comparison with dynamic contrast-enhanced and multiparametric MRI.Eur Radiol. 2021 Jan;31(1):356-367. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07094-z. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32780207 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Cancer Conspicuity on Computed Versus Acquired High b-Value Diffusion-Weighted MRI.Acad Radiol. 2021 Aug;28(8):1108-1117. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.03.011. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Acad Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32307271 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion-weighted MRI of ischemic stroke at 3T: Value of synthetic b-values.Br J Radiol. 2021 May 1;94(1121):20200869. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20200869. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Br J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33596102 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluations of the diagnostic performance of ZOOMit diffusion-weighted imaging and conventional diffusion-weighted imaging for breast lesions.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Dec 1;13(12):8478-8488. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-415. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 38106248 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of imaging conditions for dental MRI using 3T-MRI system with microscopy coil in clinical situation.Radiol Phys Technol. 2025 Jun;18(2):570-581. doi: 10.1007/s12194-025-00910-5. Epub 2025 Apr 30. Radiol Phys Technol. 2025. PMID: 40301177
References
-
- Stadlbauer A , Bernt R , Gruber S , Bogner W , Pinker K , van der Riet W , et al. . Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS) for the diagnosis of malignant and benign breast lesions . Eur Radiol 2009. ; 19 : 2349 – 56 . doi: 10.1007/s00330-009-1426-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

