Age-Related Impairment of Structure and Function of Iliac Artery Endothelium in Rats Is Improved by Elevated Fluid Shear Stress
- PMID: 31291237
- PMCID: PMC6637813
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.916287
Age-Related Impairment of Structure and Function of Iliac Artery Endothelium in Rats Is Improved by Elevated Fluid Shear Stress
Abstract
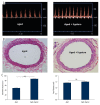
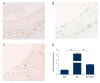
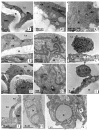
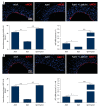
BACKGROUND Aging plays an important role in endothelial dysfunction. Fluid shear stress (FSS) can activate endothelial cells (ECs). Herein, we tested the hypothesis that this endothelial impairment could be improved by elevated FSS (EFSS) in aged rats. MATERIAL AND METHODS EFSS was created through ligation of the unilateral common iliac artery in 20-month-old rats, evaluated by measuring blood flow velocity with Doppler spectrum. The effect of FSS on aged ECs was examined by senescence-associated ß-galactosidase (SA-ß-Gal) staining, ultrastructural observation, and immunostaining and qPCR analysis of eNOS and SIRT1 expression on both the mRNA and protein levels. RESULTS (1) FSS was significantly increased in the right common iliac artery (RCIA) in rats with the ligation of the left common iliac artery (LCIA). (2) SA-ß-Gal staining was significantly attenuated by EFSS in the RCIA of aged rats. (3) Ultrastructural observation showed that ECs in the RCIA of normal aged rats became irregular and enlarged, with increasingly polypoid nuclei and fewer mitochondria, whereas ECs in the RCIA of aged rats with LCIA ligation became more prominent and contained more mitochondria. (4) eNOS and SIRT1 expression in the RCIA of aged rats with LCIA ligation was significantly upregulated compared with that in control group rats. CONCLUSIONS The present study for the first time shows that EFSS has the ability to improve age-related impairment of endothelial structure and functions.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Bonetti PO, Lerman LO, Lerman A. Endothelial dysfunction: A marker of atherosclerotic risk. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2003;23:168–75. - PubMed
-
- Widlansky ME, Gokce N, Keaney JF, Vita JA. The clinical implications of endothelial dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;42:1149–60. - PubMed
-
- Furchgott RF, Zawadzki JV. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980;288:373–76. - PubMed
-
- Busse R, Fleming I. Vascular endothelium and blood flow. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;(176 Pt 2):43–78. - PubMed
-
- Pober JS, Min W, Bradley JR. Mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction, injury, and death. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4:71–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

