The monetary burden of cysticercosis in Mexico
- PMID: 31291239
- PMCID: PMC6645581
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007501
The monetary burden of cysticercosis in Mexico
Abstract
Background: Taenia solium cysticercosis is a public health and agricultural problem in many low and middle-income countries where health education, sanitation, pig management practices and meat inspection infrastructure are insufficient. Cysticercosis affects both human and animal health and has important economic consequences. Very few studies have been conducted to evaluate the monetary burden of cysticercosis. This study aimed at estimating the 2015 costs associated with cysticercosis in humans and pigs in Mexico.
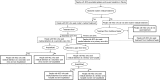
Methods: The monetary burden of human cysticercosis was estimated based on costs incurred by living with and treating epilepsy and severe chronic headaches associated with neurocysticercosis (NCC). The estimated cost of porcine cysticercosis took into consideration losses due to the reduction in the price of cysticercosis-infected animals. Epidemiologic and economic data were obtained from the published literature, government reports, and setting-specific questionnaires. Latin hypercube sampling methods were employed to sample the distributions of uncertain parameters and to estimate 95% credible regions (95% CRs). All results are reported in 2015 U.S.$.
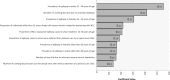
Findings: The overall monetary burden associated with NCC morbidity was estimated at U.S.$215,775,056 (95% CR U.S.$109,309,560 -U.S.$361,924,224), with U.S.$436 (95% CR: U.S.$296 -U.S.$604) lost per patient. If loss of future years of income and productivity due to NCC-associated deaths was included, this value increased by U.S.$54.26 million, assuming that these individuals earned Mexico's median wage salary. An additional U.S.$19,507,171 (95% CR U.S.$5,734,782 -U.S.$35,913,487) was estimated to be lost due to porcine cysticercosis.
Conclusions: This study suggests that T. solium cysticercosis results in considerable monetary losses to Mexico.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The societal cost of Taenia solium cysticercosis in Tanzania.Acta Trop. 2017 Jan;165:141-154. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2015.12.021. Epub 2016 Jan 3. Acta Trop. 2017. PMID: 26756713
-
Estimation of the cost of Taenia solium cysticercosis in Eastern Cape Province, South Africa.Trop Med Int Health. 2006 Jun;11(6):906-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01627.x. Trop Med Int Health. 2006. PMID: 16772013
-
The disease burden of Taenia solium cysticercosis in Cameroon.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009;3(3):e406. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000406. Epub 2009 Mar 31. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009. PMID: 19333365 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of the health and economic burden of neurocysticercosis in India.Acta Trop. 2017 Jan;165:161-169. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.01.017. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Acta Trop. 2017. PMID: 26802489
-
Mapping occurrence of Taenia solium taeniosis/cysticercosis and areas at risk of porcine cysticercosis in Central America and the Caribbean basin.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Sep 18;10(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2362-7. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 28923090 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SPDB: a specialized database and web-based analysis platform for swine pathogens.Database (Oxford). 2020 Jan 1;2020:baaa063. doi: 10.1093/database/baaa063. Database (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 32761141 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual dimorphism in the murine model of extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis.Parasitol Res. 2023 Sep;122(9):2147-2154. doi: 10.1007/s00436-023-07913-4. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Parasitol Res. 2023. PMID: 37428312
-
A Large Case Series of Neurocysticercosis in Kuwait, a Nonendemic Arabian Gulf Country in the Middle East Region.Microorganisms. 2021 Jun 4;9(6):1221. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061221. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34199952 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical characterization and gene structure analysis of the 24-kDa glutathione transferase sigma from Taenia solium.FEBS Open Bio. 2024 May;14(5):726-739. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13795. Epub 2024 Mar 21. FEBS Open Bio. 2024. PMID: 38514457 Free PMC article.
-
Mortality in Parenchymal and Subarachnoid Neurocysticercosis.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2021 Jul 7;105(1):176-180. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-1330. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2021. PMID: 34232912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhattarai R, Carabin H and Budke CM (2013). The Burden of Cysticercosis, Novel Aspects on Cysticercosis and Neurocysticercosis, Prof. Humberto Foyaca Sibat (Ed.), InTech, 10.5772/51668 Available from: https://www.intechopen.com/books/novel-aspects-on-cysticercosis-and-neur... - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

