Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with elevated alanine aminotransferase in patients receiving asunaprevir plus daclatasvir combination therapy for chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 31291311
- PMCID: PMC6619746
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219022
Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with elevated alanine aminotransferase in patients receiving asunaprevir plus daclatasvir combination therapy for chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
Aims: Drug-induced liver damage characterized by serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation often occurs in direct-acting antiviral (DAA) combination therapy for chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. This study explored single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at drug metabolism- or transport-related genes that were associated with ALT elevation in asunaprevir plus daclatasvir therapy.
Methods: Subjects were 185 Japanese patients with chronic HCV genotype 1b infection who received asunaprevir plus daclatasvir therapy. Tag SNPs at possible metabolizing enzyme and transporter genes, which were involved in the pharmacokinetics of asunaprevir and daclatasvir, were selected.
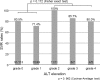
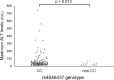
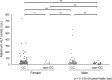
Results: Among the tag SNPs analyzed, CYP3A4 rs4646437 was significantly associated with ALT elevation (p = 0.013): maximum ALT values in patients with genotype CC were higher than those in patients with genotype non-CC (allele T). The proportion of grades 2-4 in genotype CC patients were significantly greater than those in genotype non-CC patients (p = 0.028). No patients with genotype non-CC showed grade ≥2 ALT elevation. In multivariate analysis, rs4646437 genotype CC and cirrhosis were significant, independent factors associated with grade ≥1 ALT elevation (odds ratio, 2.83 and 1.88; p = 0.040 and 0.045, respectively). In exploratory analyses, although serum concentrations of asunaprevir and daclatasvir were not correlated with maximum ALT values or rs4646437 genotypes, asunaprevir concentrations in patients with grade ≥1 ALT elevation were significantly higher than those in patients with grade <1 ALT elevation (P = 0.023).
Conclusions: CYP3A4 rs4646437 was found to be significantly and independently associated with ALT elevation in Japanese patients receiving ASV plus DCV therapy. Notably, none of the patients with rs4646437 genotype non-CC (allele T) had grade ≥2 ALT elevation. SNP genotyping prior to treatment might be useful for carefully monitoring patients to complete treatment safely.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association between alanine aminotransferase elevation and UGT1A1*6 polymorphisms in daclatasvir and asunaprevir combination therapy for chronic hepatitis C.J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jun;53(6):780-786. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1405-3. Epub 2017 Nov 1. J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29094205
-
Relationships between serum asunaprevir concentration and alanine aminotransferase elevation during daclatasvir plus asunaprevir for chronic HCV genotype 1b infection.J Med Virol. 2016 Mar;88(3):506-11. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24360. Epub 2015 Aug 27. J Med Virol. 2016. PMID: 26292191
-
Randomized trial of daclatasvir and asunaprevir with or without PegIFN/RBV for hepatitis C virus genotype 1 null responders.J Hepatol. 2014 Mar;60(3):490-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.10.019. Epub 2013 Oct 26. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24444658 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of a fixed dose combination tablet of asunaprevir + beclabuvir + daclatasvir for the treatment of Hepatitis C.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Feb;21(3):261-273. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2019.1697674. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31914336 Review.
-
Asunaprevir plus daclatasvir for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection.Drugs Today (Barc). 2015 Nov;51(11):629-43. doi: 10.1358/dot.2015.51.11.2414528. Drugs Today (Barc). 2015. PMID: 26744738 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Susceptibility to Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis Virus Infection.Viruses. 2023 Feb 17;15(2):559. doi: 10.3390/v15020559. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of CYPs and Transporters in the Biotransformation and Transport of the Anti-hepatitis C Antiviral Agents Asunaprevir, Daclatasvir, and Beclabuvir: Impact of Liver Disease, Race and Drug-drug Interactions on Safety and Efficacy.Curr Drug Metab. 2024;25(2):96-109. doi: 10.2174/0113892002288832240213095622. Curr Drug Metab. 2024. PMID: 38441017 Review.
References
-
- Maekawa S, Sato M, Kuratomi N, Inoue T, Suzuki Y, Tatsumi A, et al. Association between alanine aminotransferase elevation and UGT1A1*6 polymorphisms in daclatasvir and asunaprevir combination therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol. 2018;53:780–786. Epub 2017 Nov 1. 10.1007/s00535-017-1405-3 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

