The effectiveness of intensity-modulated radiation therapy versus 2D-RT for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31291379
- PMCID: PMC6619803
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219611
The effectiveness of intensity-modulated radiation therapy versus 2D-RT for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: At present, the management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is mainly based on radiotherapy, but there are many radiation delivery techniques such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and 2-dimensional radiotherapy (2D-RT).
Materials and methods: We searched all the eligible studies through the PubMed, Cochrane Library, Medline, and Embase. The endpoint events in meta-analysis were overall survival (OS), tumor local control including local-regional free survival (LRFS), progression-free survival (PFS), and distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), and late toxicities.
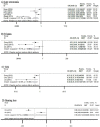
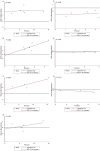
Results: A total of ten publications met the criteria and were identified through searches of the databases and references. We included 13304 patients in the meta-analysis, of whom 5212 received IMRT and 8092 were allocated to 2D-RT alone group. Compared with 2D-RT treatment, the IMRT group was associated with a better 5-year OS (OR = 1.70; 95% CI = 1.36-2.12), LRFS (OR = 2.08; 95% CI = 1.82-2.37), and PFS (OR = 1.40; 95% CI = 1.26-1.56). Additionally, the incidence of late toxicities such as late xerostomia (OR = 0.21; 95% CI = 0.09-0.51), trismus (OR = 0.16; 95% CI = 0.04-0.60), and temporal lobe neuropathy (TLN) (OR = 0.40; 95% CI = 0.24-0.67) for NPC patients in IMRT group were significantly lower than 2D-RT.
Conclusions: The meta-analysis demonstrates that IMRT provides improved long-term tumor overall survival and local control including LRFS and PFS. Additionally, IMRT yields a lower incidence of late toxicities induced by irradiation in NPC patients. Compared to 2D-RT, IMRT may be an effective treatment for patients with NPC. Further intensive studies should be pursued to examine the association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Gluckman J, Portugal L (1995) Photodynamic therapy for cancer of the head and neck. Cancer Treat Res 74: 159–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

