The Role of the EGF Receptor in Sex Differences in Kidney Injury
- PMID: 31292196
- PMCID: PMC6727256
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2018121244
The Role of the EGF Receptor in Sex Differences in Kidney Injury
Abstract
Background: Sex differences mediating predisposition to kidney injury are well known, with evidence indicating lower CKD incidence rates and slower decline in renal function in nondiabetic CKD for premenopausal women compared with men. However, signaling pathways involved have not been elucidated to date. The EGF receptor (EGFR) is widely expressed in the kidney in glomeruli and tubules, and persistent and dysregulated EGFR activation mediates progressive renal injury.
Methods: To investigate the sex differences in response to renal injury, we examined EGFR expression in mice, in human kidney tissue, and in cultured cell lines.
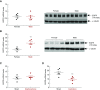
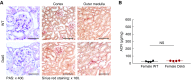
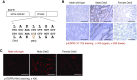
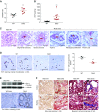
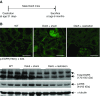
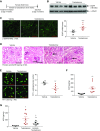
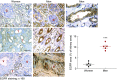
Results: In wild type mice, renal mRNA and protein EGFR levels were comparable in males and females at postnatal day 7 but were significantly lower in age-matched adult females than in adult males. Similar gender differences in renal EGFR expression were detected in normal adult human kidneys. In Dsk5 mutant mice with a gain-of-function allele that increases basal EGFR kinase activity, males had progressive glomerulopathy, albuminuria, loss of podocytes, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis, but female Dsk5 mice had minimal kidney injury. Oophorectomy had no effect on renal EGFR levels in female Dsk5 mice, while castration protected against the kidney injury in male Dsk5 mice, in association with a reduction in EGFR expression to levels seen in females. Conversely, testosterone increased EGFR expression and renal injury in female Dsk5 mice. Testosterone directly stimulated EGFR expression in cultured kidney cells.
Conclusions: These studies indicate that differential renal EGFR expression plays a role in the sex differences in susceptibility to progressive kidney injury that may be mediated at least in part by testosterone.
Keywords: DSK5; EGFR; glomerulosclerosis; testosterone; tubulointerstitial fibrosis.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures




Similar articles
-
EGFR drives the progression of AKI to CKD through HIPK2 overexpression.Theranostics. 2019 Apr 13;9(9):2712-2726. doi: 10.7150/thno.31424. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31131063 Free PMC article.
-
Erlotinib attenuates the progression of chronic kidney disease in rats with remnant kidney.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018 Apr 1;33(4):598-606. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfx264. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018. PMID: 28992288
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor plays a role in the regulation of liver and plasma lipid levels in adult male mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Mar 1;306(5):G370-81. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00116.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24407590 Free PMC article.
-
Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in acute and chronic kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2013 May;83(5):804-10. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.435. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23325080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Its Ligands in Kidney Inflammation and Damage.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Dec 23;2018:8739473. doi: 10.1155/2018/8739473. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30670929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revealing active components, action targets and molecular mechanism of Gandi capsule for treating diabetic nephropathy based on network pharmacology strategy.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Nov 23;20(1):362. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-03155-4. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 33228635 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR-mediated activation of adipose tissue macrophages promotes obesity and insulin resistance.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 10;13(1):4684. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32348-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35948530 Free PMC article.
-
The role of gender disparities in kidney injury.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Apr;8(7):514. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.01.23. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32395558 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Proximal tubular epithelial insulin receptor mediates high-fat diet-induced kidney injury.JCI Insight. 2021 Feb 8;6(3):e143619. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.143619. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 33400689 Free PMC article.
-
EGF receptor-mediated FUS phosphorylation promotes its nuclear translocation and fibrotic signaling.J Cell Biol. 2020 Sep 7;219(9):e202001120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202001120. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32678881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neugarten J, Acharya A, Silbiger SR: Effect of gender on the progression of nondiabetic renal disease: A meta-analysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 11: 319–329, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Yu M, Ryu DR, Kim SJ, Choi KB, Kang DH: Clinical implication of metabolic syndrome on chronic kidney disease depends on gender and menopausal status: Results from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination survey. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25: 469–477, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Maric-Bilkan C: Sex differences in micro- and macro-vascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Clin Sci (Lond) 131: 833–846, 2017 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

