Performance of GFR Slope as a Surrogate End Point for Kidney Disease Progression in Clinical Trials: A Statistical Simulation
- PMID: 31292198
- PMCID: PMC6727266
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2019010009
Performance of GFR Slope as a Surrogate End Point for Kidney Disease Progression in Clinical Trials: A Statistical Simulation
Abstract
Background: Randomized trials of CKD treatments traditionally use clinical events late in CKD progression as end points. This requires costly studies with large sample sizes and long follow-up. Surrogate end points like GFR slope may speed up the evaluation of new therapies by enabling smaller studies with shorter follow-up.
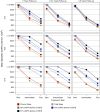
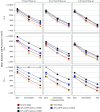
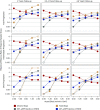
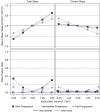
Methods: We used statistical simulations to identify trial situations where GFR slope provides increased statistical power compared with the clinical end point of doubling of serum creatinine or kidney failure. We simulated GFR trajectories based on data from 47 randomized treatment comparisons. We evaluated the sample size required for adequate statistical power based on GFR slopes calculated from baseline and from 3 months follow-up.
Results: In most scenarios where the treatment has no acute effect, analyses of GFR slope provided similar or improved statistical power compared with the clinical end point, often allowing investigators to shorten follow-up by at least half while simultaneously reducing sample size. When patients' GFRs are higher, the power advantages of GFR slope increase. However, acute treatment effects within several months of randomization can increase the risk of false conclusions about therapies based on GFR slope. Care is needed in study design and analysis to avoid such false conclusions.
Conclusions: Use of GFR slope can substantially increase statistical power compared with the clinical end point, particularly when baseline GFR is high and there is no acute effect. The optimum GFR-based end point depends on multiple factors including the rate of GFR decline, type of treatment effect and study design.
Keywords: CKD progression; GFR slope; end stage kidney disease; simulation studies.
Copyright © 2019 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


References
-
- Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF III, Feldman HI, et al. .: CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration) : A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate [published correction appears in Ann Intern Med 155: 408, 2011]. Ann Intern Med 150: 604–612, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Levey AS, Coresh J: Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 379: 165–180, 2012 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

