A human liver cell atlas reveals heterogeneity and epithelial progenitors
- PMID: 31292543
- PMCID: PMC6687507
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1373-2
A human liver cell atlas reveals heterogeneity and epithelial progenitors
Abstract
The human liver is an essential multifunctional organ. The incidence of liver diseases is rising and there are limited treatment options. However, the cellular composition of the liver remains poorly understood. Here we performed single-cell RNA sequencing of about 10,000 cells from normal liver tissue from nine human donors to construct a human liver cell atlas. Our analysis identified previously unknown subtypes of endothelial cells, Kupffer cells, and hepatocytes, with transcriptome-wide zonation of some of these populations. We show that the EPCAM+ population is heterogeneous, comprising hepatocyte-biased and cholangiocyte populations as well as a TROP2int progenitor population with strong potential to form bipotent liver organoids. As a proof-of-principle, we used our atlas to unravel the phenotypic changes that occur in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and in human hepatocytes and liver endothelial cells engrafted into a mouse liver. Our human liver cell atlas provides a powerful resource to enable the discovery of previously unknown cell types in normal and diseased livers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
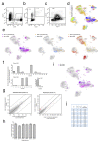
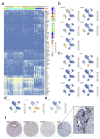
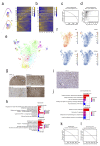
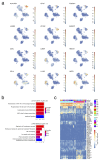
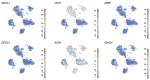

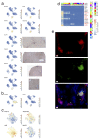
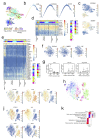
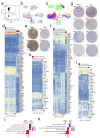


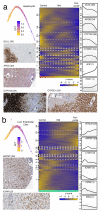
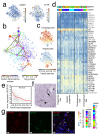
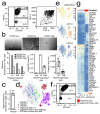
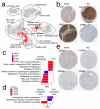
Comment in
-
Mapping the cells in the liver - unchartered subtypes and heterogeneity.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Sep;16(9):513. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0192-0. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31363179 No abstract available.
References
-
- Michalopoulos GK, DeFrances MC. Liver regeneration. Science. 1997;276:60–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

