Imaging biomarkers for the treatment of esophageal cancer
- PMID: 31293338
- PMCID: PMC6603816
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i24.3021
Imaging biomarkers for the treatment of esophageal cancer
Abstract
Esophageal cancer is known as one of the malignant cancers with poor prognosis. To improve the outcome, combined multimodality treatment is attempted. On the other hand, advances in genomics and other "omic" technologies are paving way to the patient-oriented treatment called "personalized" or "precision" medicine. Recent advancements of imaging techniques such as functional imaging make it possible to use imaging features as biomarker for diagnosis, treatment response, and prognosis in cancer treatment. In this review, we will discuss how we can use imaging derived tumor features as biomarker for the treatment of esophageal cancer.
Keywords: Computed tomography perfusion; Diffusion-weighted imaging; Dynamic-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging; Esophageal cancer; Positron emission tomography; Texture analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: We confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication, and there has been no significant financial support for this work that may have influence on the contents.
Figures
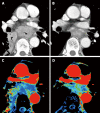
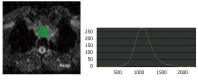
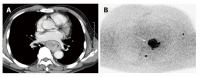
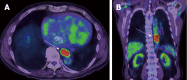
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Wang Z, Liu XY, Liu FY. Recurrence pattern of squamous cell carcinoma in the middle thoracic esophagus after modified Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy. World J Surg. 2007;31:1107–1114. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa S, Kanda T, Kosugi S, Ohashi M, Suzuki T, Hatakeyama K. Recurrence pattern of squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus after extended radical esophagectomy with three-field lymphadenectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2004;198:205–211. - PubMed
-
- Axel L. Cerebral blood flow determination by rapid-sequence computed tomography: Theoretical analysis. Radiology. 1980;137:679–686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

